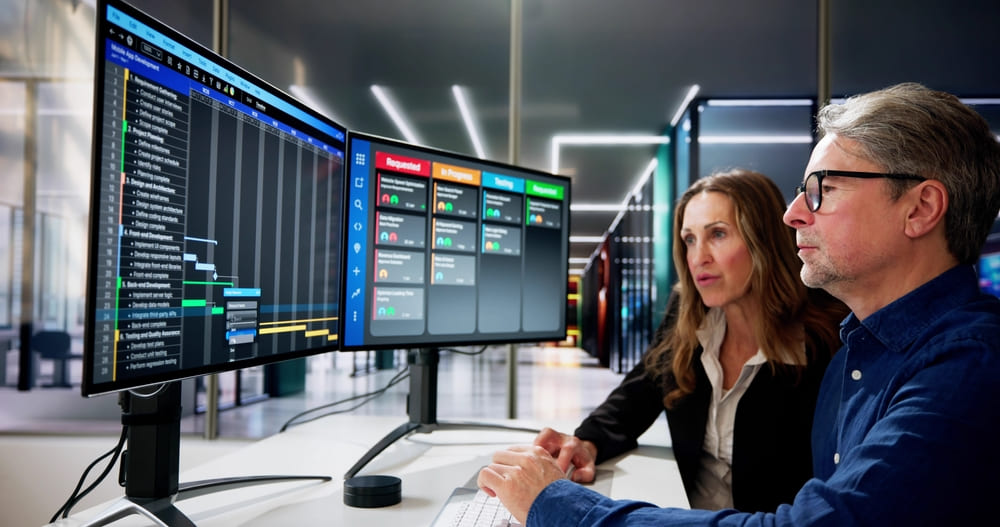
In project management world, going agile is the essence. The agile planning process is iterative and flexible, and emphasizes the need to constantly get feedback from end customers to adapt and evolve projects dynamically. This is what agile scheduling is all about—helping teams to turn around quickly when they meet new challenges and deliver work in iterations. This article will guide you through the key aspects of agile scheduling, such as timeboxing and iterative cycles, sprint planning and daily stand-ups which are all major components of agile planning of the project.
Find the ways to use these ideas to keep the momentum and to make sure that continuous improvement will be happening in your projects, which means to apply agile project planning to create a dynamic project management through timeboxing, iterative cycles, sprint planning, and daily stand-ups.
Key Takeaways
- Agile scheduling emphasizes continuous adaptation and improvement through iterative cycles, timeboxing, and integration of feedback, contrasting with traditional project management methods that utilize rigid schedules and fixed milestones.
- Sprint planning is a key element of Agile scheduling, focusing on defining sprint goals, selecting user stories for sprints, and allocating tasks with story points to team members, ensuring everyone has a clear understanding of their roles and responsibilities.
- Agile project management leverages tools such as agile boards, Gantt charts, and digital Agile tools to streamline processes and enhance collaboration, alongside daily stand-ups to maintain effective communication and quick adaptation to project changes.
The Agile Scheduling Paradigm
Flexible scheduling is a major deviation from the conventional project management approaches. Agile projects are marked by iterative or incremental approach to work as opposed to a linear cycle, which makes it possible to improve and adapt at any stage of the project life. Such an iterative strategy allows teams to learn from each iteration, take feedback, and change their approaches. In the general agile project management process, agile planning is an essential aspect of promoting such continuous adaptation through features such as fast feedback loops, active release cycles and ongoing planning.
This approach is very different from traditional project management practices that are characterized by preplanning and control of works with the use of the established methods and tools. Traditional projects use more rigid approaches, however, Agile gives the flexibility to change priorities over sticking to the originally planned path. The continuous adaptation according to newly acquired information brought in during each phase of an agile project’s life span allows team members to work closely with the stakeholders while including all the useful understandings for the next phases to yield the most optimal results that would please everybody.
Crafting an Agile Project Timeline
The development of flexibility of the project schedule depends on the successful implementation of timeboxing methodologies, iterative cycles, and the inclusion of project milestones and release dates into the schedule of the project. All the components act in tandem to produce a dynamic, flexible and competent plan that propels the project to the intended goals.
Timeboxing Techniques
Timeboxing is one of the most important elements of Agile scheduling whereby the project schedule gets divided into smaller sprints or iterations. This approach creates an element of urgency and emphasizes the need to do the most important tasks through reduced demand from other activities. It helps the project managers to work with the time and resources of their team to succeed in goals within the limits of time set for the project.
Establishing Iterative Cycles
Agile schedules are planned through a sequence of iterative phases, in the Agile scheduling approach. The aforementioned iterative cycles are agile iterations, where planning, development, testing, evaluation, and sometimes design as well as deployment activities are performed within a given time frame. In this way, teams constantly cycling through these iterations manage to refine their work and deal with issues as they surface.
The importance of the project manager lies in leading the team through this process of managing multiple projects at the same time, called project portfolio management. This requires to develop a learning and adaptation culture in the team.
In practice, in this approach every individual iteration leads to success in larger projects by permitting constant finetuning until all goals have been achieved.
Integrating Milestones and Release Dates
The milestones and release dates are an important part of the timeline of an agile project, being the indicators of the progress completion and presence of deliverables. This helps to evaluate the progress, identify important events, and maintain the project in line with the objectives. To do this integration properly, the product vision should be defined at the very beginning, features should be prioritized in the product backlog, a planning meeting should be carried out using a Scrum method and a product release calendar should be confirmed and distributed to stakeholders.
Such approach is quite different from the usual project management methodologies, which are based on tight schedules with deadlines at fixed milestones.
Further Reading: Mastering Agile Methodologies: Ultimate Guide To Transformative Project Management
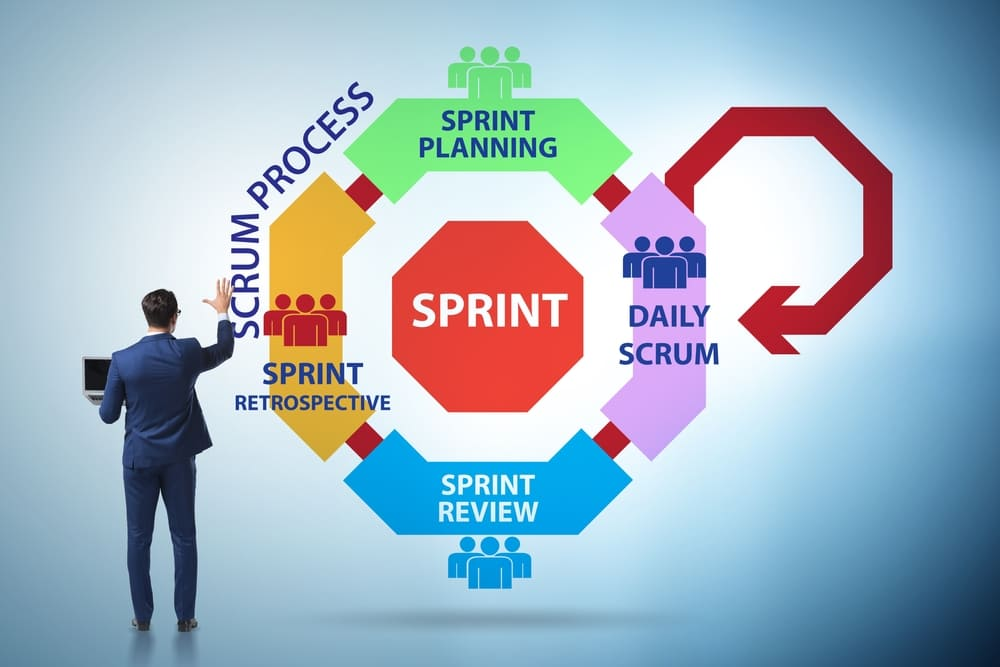
The Anatomy of Sprint Planning
Sprint planning is the heart of agile scheduling, in which the goals for each sprint are defined, the user stories are selected, and the story points and tasks are allocated to members of the team. These components are essential in leading the project towards its set goals and making sure all team members have a clear idea of their tasks.
Defining Sprint Goals
Sprint goals, which are planned by the team together, act as the major driver for all sprints. They present a shared goal that serves to orient the team to their goals. The goals play a critical role in fueling inspiration and orientation among every member of the team. It is important to make sure that these aims are achieved according to SMART criteria- Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant and Time-bound.
These team-generated sprint goals had to be specific, but also attainable so that the progress towards them could be easily monitored. Pursuing them should not appear difficult. They have to find a trade off of a challenging but feasible project with resource constraints, and that also remain relevant to the overall project objectives will keep everybody focused on the outcomes most closely related to the desired and or expected results. Lastly, they need to be time-bound, that is to say, to set time limits that indicate certain points in time or cutoffs, when the sprints are accomplished, what tasks are finished.
Selecting User Stories
According to the Agile approach, user stories are selected for a sprint by making them a part of the sprint backlog during the planning phase. It is worth mentioning that priority and estimated effort of these user stories are considered when making this choice. User stories reflect end-user demands and are traced by using burn-down charts which represent their progress during the sprint.
Assigning Story Points and Tasks
In the sprint planning process, it is important to allocate story points and tasks to every team member. They are the approximations of the amount of work needed to finish a user story from a product backlog. Distribution of these points clarifies the individual roles, which are then shared among team members.
Each user story will be considered during development by delegating tasks based on assigned story points. This fosters a feeling of belonging and accountability within the team and fosters cooperation among its members.
Road mapping and Release Planning in Agile Projects
Agile scheduling encompasses the combination of road mapping and release planning. In a few words, roadmap refers to development of a flexible strategic plan which lists future product releases, epics and features. However, release planning aims at synchronization of these releases with business value in context of dynamic requirements. Collectively, these elements set a clear way forward for the agile team to implement in their work.
Constructing the Product Roadmap
Developing a product roadmap is a vital strategic task that outlines the long-term vision for the product. It involves an ongoing and repetitive process of:
- Examining market trends
- Aligning with company objectives
- Incorporating customer input
- Considering technical limitations
Instead of focusing on individual features, it’s important to prioritize outcomes and themes in order to create a high-level strategic plan for the project’s future direction.
Aligning Releases with Business Value
The secret of releasing according to business value is giving priority to the most valuable features and delivering them first. This needs an evaluation of the probable affect of each feature on the business and putting them in order of priority.
Releases tied to business value ensures that any outputs generated are aimed at supporting the strategic objectives of the company. This makes sure that resources are allocated properly so that the maximum returns are realized by the organization.
Adapting to Evolving Requirements
The fast-moving world of Agile requires the skills to change requirements. This involves being flexible to changes in customer requirements, market dynamics, or project constraints, and to adjust the project plan as necessary. Change embracing ensures that their projects are applicable in the current scenario, beneficial and in the pace of the days business environment.
Balancing Workloads and Resources
Balance of workloads and resources is an important part of Agile scheduling. The key aim is to maintain a balance in which the team members do not have too many tasks to handle while ensuring the efficient use of resources. This entails managing the synergy within cross-functional teams and also the sharing of resources among them so that scope creep does not happen.
Cross-Functional Team Dynamics
Cross-functional teams are the cornerstone of Agile schedule, being based in a team’s collaboration and problem-solving capabilities. Such teams are made up of people having different skills and information, which creates an innovative friendly space.
Effective management of project teams can dramatically increase the performance of the project and contribute to its success. Through harnessing the abilities and knowledge in these varied teams, projects can be pushed to achievements.
Managing Shared Resources
The maintenance of common resources calls for a fine balance. The completion of the task, therefore, involves ensuring that all team members have a good access, no inhibitors to progress, strategic decision making and resource allocation. Monitoring should be continuous to ensure effective utilization of the available resources.
Preventing Scope Creep
Control of scope creep is one of the key elements of Agile scheduling whereby very clear project boundaries are set, and any movements to expand the scope beyond those frontiers are monitored on a daily basis. This method ensures that teams continue to concentrate on completing project goals and minimize unnecessary delays and complications that may result from an enlarged scope.
Further Reading: Enhancing Agility With Agile Project Portfolio Management
Agile Project Management Tools and Techniques
The supporting tools and techniques are rather diverse from the project management methodology of an agile project management. They include agile boards and Gantt charts that make the information more visible. These tools are crucial to the execution of activities and nurturing effective teamwork within an agile project environment.
Utilizing Agile Boards
In project management, a world of Agile boards comes up as a set of instruments which include the Scrum board as well as the Kanban board. They are a graphical presentation of progress of a project, to allow teams to monitor their activities, notice any obstacles, and implement required adjustments to meet their success.
Incorporating Gantt Charts for Visibility
Gantt charts provide a visual representation of the project schedule, giving a snapshot of its flow, interrelations, and due dates. You can track the project status by using the Gantt charts in an Agile schedule so that you can make smart moves for efficient management during all stages.
Embracing Digital Agile Tools
The use of agile tools has altered the way that people in Agile teams now behave. They encourage communication flow, foster team building among members, and give instant updates to everybody as to what is going on.
An agile project management tool enables tracking of the progress and automation of routine tasks, thus, gaining efficiency and productivity of Agile projects management. With its support ready, flexible teams will perform their tasks effectively, thereby boosting the output in a shorter time than the regular methods.
Navigating Daily Stand-Ups and Communication
The smooth running of the project is hinged on frequent communication and daily stand-ups in Agile timetable. Team members use these brief daily meetings to give progress reports, discuss obstacles, and plan activities for the day.
Conducting Effective Stand-Ups
The effectiveness of Agile managing rests on the performance of proper stand up meetings. These meetings should be brief, focused, and utilized as a means of team members providing updates, discussing problems, and deciding on their daily tasks. Through a structured format, focusing on three vital questions. What have we accomplished since the last meeting? What tasks are planned for today? Are there any hurdles or issues? – Teams can make sure that their stand-up meetings are useful.
Enhancing Team Collaboration
Encouraging the team work is an essential feature of Agile scheduling. This creates camaraderie and productive environment for the team members to share ideas, solve problems, and achieve their goals. Effective communication, clear goals, collaboration tools, and a supportive culture within the team are some ways to enhance team collaboration in Agile scheduling.
Leveraging Real-Time Updates
Real-time updates are a must in Agile environments so that the pace is not lost. Such updates are fundamental for the whole team to be aware of everything and act accordingly should any changes or issues occur. By employing digital tools and a variety of communication mediums, these updates are facilitated, therefore, enhancing the team’s ability to respond effectively.
Summary
Agile scheduling is an innovative project management method that offers many advantages compared to the old-fashioned methodologies. It fosters continuous learning, adaptability and progress to help teams to deliver value in an efficient and effective way. Each practice of Agile scheduling such as the flexible project timelines development, cross-disciplinary teams management, digital tools’ flexibility and effective stand-up meetings is aimed at productivity and teamwork.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is Agile schedule?
Agile schedule means dividing the project planning into the timeboxes instead of creating a plan for the whole project duration.
How do you manage schedules in Agile?
In Agile approach, project management is based on division of project planning into small time intervals or “timeboxes” that are spaced out throughout the project duration. It gives more flexibility and adaptability in scheduling to complete the entire project.
What are some beneficial tools and techniques in Agile project management?
Efficient ways of managing an Agile project include tools like Agile boards, Gantt charts as well as digital resources to improve the coordination and efficiency of the project as a whole. Using these methodologies can dramatically improve the efficiency of a team while working within an agile approach.
How does Agile scheduling prevent scope creep?
The challenge of scope creep is solved through an agile schedule which will make sure that well-defined project boundaries are set and any attempt to expand these boundaries are closely monitored. This method offers a great tool to keep the concentration of the project and to avoid the useless inclusions or changes.
What is the purpose of a stand-up meeting in Agile scheduling?
In Agile scheduling, a stand-up meeting is primarily aimed at giving team members a chance to present progress updates, to discuss any issues they may be encountering and plan their daily goals. This helps to promote unity within the team while ensuring that all members of the team are focused on achieving the set goals.