What is business agility, and why is it so important in our fast-paced business environment today? Agile organizations represent business agility that is characterized by quick adaptability to changes, innovation at speed, and competitiveness in the face of disruption, much like agile businesses that demonstrate this ability through their continuous improvement and problem-solving capabilities. It is a pragmatic paradigm that has outlived its software development inception to evolve as a fundamental enabler of contemporary business resilience. This article presents the business agility definition, its main components, and the ways companies can succeed in the journey towards truly agile business in a highly uncertain business environment.
Key Takeaways
- Business agility is an organization’s ability to adapt quickly to market changes by embracing principles such as rapid response to feedback, flexibility, and adaptability, which are critical for maintaining competitiveness amid digital disruption.
- The journey to achieving business agility involves stages from acting as adaptive networks to measuring progress with specific indicators, and requires developing agile organizations that integrate next-generation technology with a focus on value stream mapping and customer feedback for continuous improvement.
- Organizational agility is reinforced by fostering a culture of innovation, investing in digital transformation, and adopting an Agile Operating Model that encourages self-organized teams, employs agile tools for real-time collaboration, and emphasizes customer-centric product development and continuous learning.
Decoding Business Agility
Agility in business is a characteristic of an organization that enables it to change quickly with the market and remain competitive within the digital disruption era. This idea came from activities in agile frameworks employed in the development of software that are supposed to control the unpredictable results and evolving requirements.
Business agility adoption permits an organization to quickly react to feedback, making them to continuously deliver value for customers and ultimately enabling them to have a competitive advantage over their opponents. Knowledge of the business context that includes organizational, company, client, technology, and solution factors is a key to successful business agility implementation that implies smooth and convenient adaptation to the changes in production and market in a productive and cost-effective way.

The Essence of Business Agility
A nimble and flexible organization is what thrives in constant change by seizing new opportunities and adapting to customer needs. Agility goes far beyond velocity alone. It involves flexibility, which is important for organizations to keep their consumers in the changing market of today.
Key Components of Agile Organizations
Agile organizations are characterized by five distinct characteristics:
- They function as networks made up of agile teams.
- Their values include alignment, accountability, expertise, transparency, and collaboration.
- Quick decision-making processes and continuous learning cycles take priority for these organizations.
- They prioritize taking swift action with 70% certainty rather than delayed action with complete certainty.
Next-generation technology has been embedded into every facet of agile organizations operations, and this has further increased their ability to create value as well as respond quickly to changes. The North Star is the common purpose or vision that anchors these entities and puts stakeholders at the heart of all decisions. Agile organizations also target a sustainable work rate that supports even productivity and quality output, and the welfare of the team has to remain intact.
Further Reading: Mastering Agile Methodologies: Ultimate Guide To Transformative Project Management
The Journey to Achieving Business Agility
Organizations grow, and in the process, the inherent dichotomy between a growing hierarchical structure and an interactive entrepreneurial network appears. Such pressure is usually the cause of the latter’s suppression. For the hybrid-work era, in this specific business environment, having a clear way of getting to agility is vital for organizations as they deal with the ever-changing circumstances.
Becoming agile is a path of being able to adjust easily to a continuous flow of challenges and so remains reactive and in step with the changes occurring around. This capability of nimbleness is not only related to survival but also to gaining a momentary competitive edge in a volatile market place and sets the platform for becoming and staying a market leader through constant innovation and adaptability.
Stages of the Business Agility Journey
Business agility is often kicked off through the networked business operating in extremely flexible ways to respond immediately to customer demands and new opportunities. Usually, one interdisciplinary team conducts the initial experiments in Agile adoption before others follow suit.

Organizations progress along this journey continuously adjusting to the changing requirements of customers by experimenting and re-evaluating priorities and closely monitoring the market that is changing rapidly.
Measuring Progress Along the Way
Checking the progress is critical to make sure that the business agility journey is going in the correct direction. Using metrics and keeping track of them on a regular basis is a guarantee that the Agile practices being implemented by an organization support the business to move into success. In order to monitor progress, critical metrics include cycle time, velocity, process efficiency, and throughput.
Higher productivity levels, value delivery capacities, customer satisfaction rates, and stakeholder engagement can be considered as further indicators of the performance of agile practices within a company.
Unlocking the Value Stream: Driving Business Agility
One of the ways towards business agility lies in the recognition and implementation of the Business Agility Value Stream, which is a collection of methods that enable the organization to timely responses to opportunities or threats, thereby faster learning and beneficial results.
This way, businesses deliver value to their customers in a continuous manner by creating on-demand release capabilities. This in turn improves the overall performance and customer satisfaction due to quick action from the agile organization. The SAFe Business Agility Value Stream implementation is a core that supports a smooth transition from the stage of opportunity identification into product delivery in the shortest time to guarantee business agility and prompt response with creative business solutions.
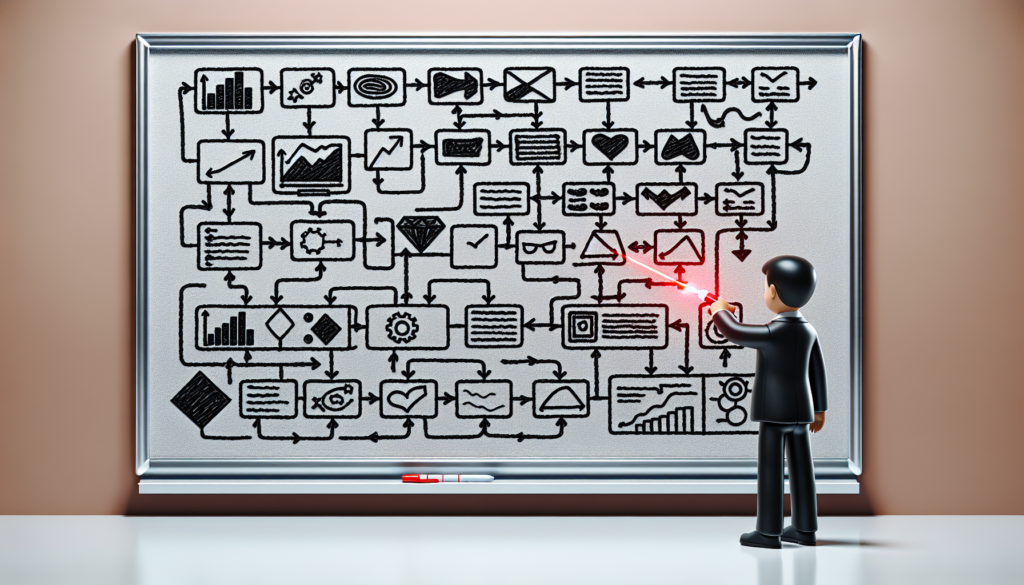
Mapping the Business Agility Value Stream
Value stream mapping is a critical exercise that includes finding, representing on the picture, examining, and improving all required steps in delivering products or services to customers. It starts with getting the right people involved, identifying the potential value streams, and choosing one for concentration.
The selected value stream is then deeply analyzed to find the areas of improvement, and all such areas are continuously worked upon by both ongoing improvements. This habit contributes greatly to the constant delivery of valuable results to our esteemed clients.
Leveraging Customer Feedback for Continuous Improvement
Feedback from the customers plays one of the most important parts in the process of value stream mapping since such feedback allows the teams to see what parts need to be addressed. Taking this important feedback into account, teams can become customer-focused in creating their products or services.
Value streams provide visibility, which is required to identify and remove obstacles, so that value reaches customers much faster. This serves to satisfy the needs of customers very quickly.
Organizational Capabilities That Enable Agility
To develop business agility, organizations need to:
- Evolve from a hierarchy of authority to a network of competence
- Prevent the formation of organizational silos
- Enhance communication
- Promote knowledge sharing
- Use agile tools to enable a sustainable pace of development
- Encourage simplicity in design and processes
- Focus on the essentials and avoid unnecessary work
This shift and the use of agile tools play a crucial role in developing true business agility.
Building a Culture of Innovation
The culture of creativity is an essential attribute in keeping the agility of the entire organization. This entails being open to industry trends and professional viewpoints as well as fostering clear communication within the organization. Establishing an atmosphere that fosters experimentation and studies from trial and error perceives failure as a vital element of creating innovative practices, hence fostering a culture of continuous enhancement.

Investing in Digital Transformation
The embrace of the digital revolution is one of the vital aspects of business agility. It enables the firms to swiftly adapt to changes in the market and seize new opportunities using flexible technological solutions. The online software has an important function in business agility in that it allows quick change to the market. Through effective sharing of real-time information and swift pivoting, the flexibility of the entire system would be improved to ensure better performance.
The Agile Operating Model: A Blueprint for Success
The business agility operating model is vital in the success journey. Agile across the organization provides fast and flexible capabilities that are critical in responding to market changes. This blueprint is a roadmap for fast and efficient adaptations in order to ensure responsiveness in dynamic markets.
From Org Chart to Agile Network
The Agile Operating Model encourages a shift from inflexible hierarchical setups to more flexible, network-style structures. These types of arrangements support:
- Quick decision-making
- Flexibility
- Versatile role definitions
- Dynamic decision-making systems
Hybrid Approach: Combining Stability with Flexibility
The hybrid approach to business agility offers a more comprehensive solution ensuring that organizations continue to enjoy the benefits of the classic hierarchical systems such as hire and scale. At the same time, it develops flexibility by means of the value stream oriented agile networks within the organizations.

Cultivating Agile Mindset Across Teams
An agile mindset among teams is achieved through a corporate culture that encourages experimentation and considers mistakes as a learning opportunity. The development of agility attributes such as being proactive, skilled, adaptable, and fast facilitates teams with the ability to easily adjust to changes in conditions.
The Role of an Agile Coach
Agile coaches play a crucial role in guiding teams towards embracing agile principles and techniques. They:
- Guarantee that the team comprehends and correctly applies agile methodologies
- Provide mentorship to individuals within the team
- Tackle any challenges or hindrances that may arise during the adoption of agile practices
- Foster an environment of continuous learning
- Assist in refining and improving existing Agile processes.
Empowering Teams for Self-Organization
Self-organizing teams are one of the critical elements of agile business promotion. Such teams function under devolved control and are flexible; they change following the contours of a directive that is not defined as such. Their strength lies in their capacity for the process of continual learning and enhancing.
In order to manage self-organizing teams properly, it is crucial to build an atmosphere where team members are encouraged, supported, and trusted. This style of leadership creates the right conditions for these teams to prosper within organizations that are pursuing more agility.
Agile Tools & Technologies: Enhancing Organizational Agility
Information technology is one of the most important factors that enable the agility concept in the organization. It is instrumental in improving the property of quick reacting and adapting to change while maintaining high productivity during software delivery. In other words, instruments that are used in agile methodologies need to promote principles of flexibility, continuous improvement, and active teamwork among members.
Selecting Tools for Real-Time Collaboration & Data Analysis
The efficient selection of Agile tools can improve team collaboration and simplify data analysis. The choice of tools should be in line with the communication preferences of the team and suited for the team size and workflow complexities. In establishing appropriate fit, one possible way is to have test periods or demos of different tools in their own working environment. Asking users for feedback ensures that the given tool works well in daily usage.
Integrating Tools into Daily Operations
An efficient choice of the right tools is necessary for smooth incorporation into the day-to-day workings to support continuous planning and flexibility in dynamic changes. This integration shall make the workflows more efficient, keep all the team members well informed, and be closely aligned with the Agile principles. These errors are opportunities for growth and adaptation in the context of Agile’s never-ending improvement philosophy.
Adapting to Customer Demands: The Agile Way
Agile organizations operate on the principle of timely delivery of customer value. Organizations are also involved in proactive customer feedback solicitation, such that they use feedback directly to guide product or service development, continuously shifting priorities and evolving offerings based on customer preferences, following the agility principles that are inherent in these entities.
Customer-Centric Product Development
A customer-oriented approach is vital in the agile development process. The customers are actively involved in the co-creation of products and services in agile organizations using such collaborative design methods as prototyping and digital feedback channels. This is where business agility value stream comes in. Using Minimum Viable Product (MVP), they quickly create and refine based on valuable customer feedback. This promotes business agility values as part of an organization’s corporate strategy for maximum development.
Continuous Learning & Adaptation
For agile companies, sunk costs are considered an investment in learning, especially when the MVP hypothesis is proven incorrect. This reflects their emphasis on adapting and learning. If the MVP ends up being successful, funding is allocated for iterative development through customer interactions and market feedback. Focus is the approach of valuing results such as return on investment and customer satisfaction rather than just finishing tasks, which is in line with the agile principles of the importance of outcomes over outputs.
Further Reading: Key Benefits of Agile Project Management Consultancy Services at PMtech Digital Solutions
Summary
Today’s rapidly changing business environment is incredibly dynamic and volatile, making agility more crucial than ever before. This multifaceted process entails nurturing creativity and adaptability within organizations, placing a strong emphasis on customer-centric product development strategies, and consistently evolving and adjusting to address new and unforeseen challenges.
As we navigate through the complexities of our ever-evolving landscape, agility stands out as the cornerstone for maintaining sustainable competitiveness, resilience, and overall prosperity in the long run.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is meant by business agility?
Business agility is the ability of a company to promptly adjust to market changes and capture feedbacks with the help of creative digital solutions. It involves swiftly responding to changes and implementing new or improved goods and services to create or redistribute value (ISO 56000: but which one (i.e. the 2016 or the 2020 standard).
What does agile mean in business?
A business’s agility is the business’s flexibility in adapting and switching in the process of sustaining prosperity in response to market shifts, customer needs, and shortened schedules.
What is an example of agility in a company?
Agility is shown in business through the use of BI services providing useful knowledge on various processes and operations. These services supply relevant information that facilitates rapid decision-making and adjustment. Through such instruments, companies can quickly evaluate their prevailing situation, enabling them to make informed decisions based on real-time data. Such flexibility makes firms remain active by altering their strategies or practices in time to their demands.
What are the key components of agile organizations?
Some of the components upon which agile organizations are built include a self-managed team network, rapid decision making mechanisms, and continuous learning cycles. They embrace a dynamic people model that encourages changes in roles and responsibilities, utilizes state-of-the-art technology, and maintains a clear guiding vision, or North Star.
Development of such elements is very important for the establishment of an agile culture in organizations. Empowering teams to make autonomous decisions and fostering perpetual learning and development, companies can be more agile in responding to market changes.
How can organizations measure progress in their journey to business agility?
Cycle time, speed, process effectiveness, output capacity, overall efficiency of tasks and projects, employee productivity, value delivered to customers, and stakeholder satisfaction—these are the critical measures that businesses can monitor to evaluate their progress in business agility. These indicators make sense in the assessment of agile practices implemented by organizations on their agile transformation trip.
By evaluating these process- and practice-related agility metrics within the company’s operations structure, it helps in measuring how successfully they have been implemented. This is crucial.















266 Responses
You are a very capable individual!
Can you be more specific about the content of your article? After reading it, I still have some doubts. Hope you can help me.
площадка для продажи аккаунтов https://birzha-akkauntov-online.ru
купить аккаунт с прокачкой https://marketplace-akkauntov-top.ru/
маркетплейс аккаунтов перепродажа аккаунтов
маркетплейс для реселлеров купить аккаунт с прокачкой
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей безопасная сделка аккаунтов
площадка для продажи аккаунтов перепродажа аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей гарантия при продаже аккаунтов
In this great design of things you’ll secure an A just for hard work. Exactly where you actually confused us was first in the particulars. You know, people say, the devil is in the details… And that could not be more accurate right here. Having said that, allow me reveal to you just what exactly did give good results. Your writing can be extremely engaging which is possibly the reason why I am making the effort to comment. I do not really make it a regular habit of doing that. Next, even though I can see a leaps in logic you come up with, I am not really confident of just how you appear to unite your details which produce the actual conclusion. For right now I will subscribe to your position but hope in the near future you link the facts better.
Online Account Store Account Sale
Guaranteed Accounts Account Sale
Account marketplace https://socialaccountsmarket2025.com
Account Buying Service Account Purchase
Account Buying Platform Sell Pre-made Account
Guaranteed Accounts Sell Account
Online Account Store Purchase Ready-Made Accounts
Sell Pre-made Account Secure Account Sales
Account marketplace Buy accounts
Account Store Account Market
Questa pagina offre il reclutamento di professionisti per compiti delicati.
I clienti possono trovare professionisti specializzati per incarichi occasionali.
Tutti i lavoratori vengono verificati con severi controlli.
ordina omicidio
Sul sito è possibile consultare disponibilità prima di procedere.
La sicurezza continua a essere la nostra priorità.
Iniziate la ricerca oggi stesso per trovare il supporto necessario!
account exchange service profitable account sales
account catalog account selling service
accounts marketplace verified accounts for sale
accounts marketplace website for buying accounts
account trading platform buycheapaccounts.com
verified accounts for sale account trading service
account market https://socialaccountsdeal.com
account selling service https://accountsmarketdiscount.com
guaranteed accounts account catalog
gaming account marketplace buy and sell accounts
accounts for sale account purchase
account market secure account sales
buy accounts ready-made accounts for sale
account exchange service buy accounts
account marketplace purchase ready-made accounts
account exchange https://social-accounts-marketplace.org/
website for buying accounts account selling service
account trading platform social media account marketplace
website for selling accounts buy and sell accounts
account purchase buy account
account exchange social media account marketplace
account exchange service account sale
account buying platform secure account sales
guaranteed accounts account exchange service
accounts marketplace ready-made accounts for sale
profitable account sales gaming account marketplace
Este site é realmente fantástico. Sempre que acesso eu encontro coisas boas Você também pode acessar o nosso site e descobrir mais detalhes! informaçõesexclusivas. Venha descobrir mais agora! 🙂
accounts market accounts marketplace
online account store https://accounts-marketplace.xyz/
profitable account sales account market
account trading service https://accounts-marketplace.live
sell accounts https://social-accounts-marketplace.xyz
account market https://buy-accounts.space
website for buying accounts https://buy-accounts-shop.pro
marketplace for ready-made accounts https://buy-accounts.live
account catalog https://accounts-marketplace.online
account marketplace accounts market
продать аккаунт akkaunty-na-prodazhu.pro
площадка для продажи аккаунтов магазины аккаунтов
купить аккаунт https://kupit-akkaunt.xyz
биржа аккаунтов https://akkaunt-magazin.online
маркетплейс аккаунтов соцсетей маркетплейсов аккаунтов
маркетплейс аккаунтов https://kupit-akkaunty-market.xyz/
покупка аккаунтов https://akkaunty-optom.live/
продажа аккаунтов https://online-akkaunty-magazin.xyz
купить аккаунт https://akkaunty-dlya-prodazhi.pro/
купить аккаунт https://kupit-akkaunt.online/
On this site, explore a variety virtual gambling platforms.
Interested in traditional options latest releases, there’s something to suit all preferences.
All featured casinos checked thoroughly to ensure security, allowing users to gamble peace of mind.
play slots
What’s more, this resource offers exclusive bonuses along with offers targeted at first-timers as well as regulars.
With easy navigation, finding your favorite casino takes just moments, saving you time.
Be in the know regarding new entries with frequent visits, as fresh options come on board often.
buy facebook ad accounts buy facebook accounts for advertising
buy fb ads account https://buy-ad-accounts.click
buy facebook ad accounts buying facebook ad account
buy facebook ads account buy facebook profile
buy fb account ad-account-buy.top
buy aged facebook ads accounts https://buy-ads-account.work
buy a facebook account buy facebook advertising accounts
В этой информационной статье вы найдете интересное содержание, которое поможет вам расширить свои знания. Мы предлагаем увлекательный подход и уникальные взгляды на обсуждаемые темы, побуждая пользователей к активному мышлению и критическому анализу!
Углубиться в тему – https://medalkoblog.ru/
buy old facebook account for ads buy facebook ad account
buy fb ads account https://ad-accounts-for-sale.work
google ads account for sale buy google ads
buy google ads accounts https://buy-ads-accounts.click
google ads agency accounts https://ads-account-for-sale.top
buy aged google ads account https://ads-account-buy.work/
On this platform, you can discover a wide selection of online slots from leading developers.
Users can try out retro-style games as well as new-generation slots with stunning graphics and interactive gameplay.
Even if you’re new or an experienced player, there’s always a slot to match your mood.
play casino
Each title are available anytime and optimized for laptops and mobile devices alike.
No download is required, so you can jump into the action right away.
Platform layout is easy to use, making it simple to browse the collection.
Join the fun, and discover the excitement of spinning reels!
On this site, you can discover a wide range of online casinos.
Whether you’re looking for classic games latest releases, you’ll find an option to suit all preferences.
Every casino included fully reviewed for safety, so you can play peace of mind.
vavada
What’s more, the site unique promotions plus incentives to welcome beginners including long-term users.
Thanks to user-friendly browsing, finding your favorite casino happens in no time, enhancing your experience.
Stay updated about the latest additions by visiting frequently, since new casinos come on board often.
sell google ads account https://buy-ads-invoice-account.top
buy aged google ads account https://buy-account-ads.work/
本站 提供 丰富的 成人材料,满足 各类人群 的 喜好。
无论您喜欢 哪种类型 的 视频,这里都 应有尽有。
所有 材料 都经过 精心筛选,确保 高品质 的 观看体验。
女同性恋者
我们支持 各种终端 访问,包括 电脑,随时随地 尽情观看。
加入我们,探索 无限精彩 的 私密乐趣。
buy verified google ads accounts https://buy-ads-agency-account.top
buy verified google ads account https://sell-ads-account.click
buy google adwords accounts https://ads-agency-account-buy.click
facebook business account for sale buy-business-manager.org
buy google ad threshold account buy-verified-ads-account.work
This website, you can access a great variety of slot machines from famous studios.
Visitors can enjoy classic slots as well as new-generation slots with high-quality visuals and interactive gameplay.
Whether you’re a beginner or a seasoned gamer, there’s always a slot to match your mood.
slot casino
All slot machines are available 24/7 and designed for PCs and mobile devices alike.
No download is required, so you can get started without hassle.
Platform layout is intuitive, making it convenient to browse the collection.
Sign up today, and dive into the excitement of spinning reels!
verified facebook business manager for sale buy-bm-account.org
buy verified bm facebook https://buy-verified-business-manager-account.org
fb bussiness manager https://buy-verified-business-manager.org
verified business manager for sale buy-business-manager-acc.org
buy facebook ads accounts and business managers business-manager-for-sale.org
verified bm for sale https://buy-business-manager-verified.org/
fb bussiness manager https://buy-bm.org
facebook bm account https://buy-business-manager-accounts.org/
buy tiktok ads https://buy-tiktok-ads-account.org
facebook bm account buy fb bm
tiktok ads account buy https://tiktok-ads-account-buy.org
buy tiktok ads account buy tiktok ads account
tiktok ads account for sale https://tiktok-agency-account-for-sale.org
tiktok ads account for sale https://buy-tiktok-ad-account.org
tiktok ads account buy https://buy-tiktok-ads-accounts.org
tiktok ads account for sale https://tiktok-ads-agency-account.org
buy tiktok ads accounts https://buy-tiktok-business-account.org
tiktok agency account for sale https://buy-tiktok-ads.org
Модные образы для торжеств этого сезона отличаются разнообразием.
Популярны пышные модели до колен из полупрозрачных тканей.
Детали из люрекса создают эффект жидкого металла.
Асимметричные силуэты определяют современные тренды.
Разрезы на юбках создают баланс между строгостью и игрой.
Ищите вдохновение в новых коллекциях — оригинальность и комфорт оставят в памяти гостей!
https://mysteryshows.com/OTRforum/viewtopic.php?t=1802
На этом сайте вы найдете подготовительные ресурсы для школьников.
Курсы по ключевым дисциплинам от математики до литературы.
Успешно сдайте тесты с помощью тренажеров.
https://crimea-news.com/other/2024/10/16/1490555.html
Примеры решений упростят процесс обучения.
Регистрация не требуется для максимальной доступности.
Используйте ресурсы дома и достигайте отличных результатов.
Трендовые фасоны сезона этого сезона задают новые стандарты.
Актуальны кружевные рукава и корсеты из полупрозрачных тканей.
Детали из люрекса создают эффект жидкого металла.
Многослойные юбки становятся хитами сезона.
Особый акцент на открытые плечи придают пикантности образу.
Ищите вдохновение в новых коллекциях — оригинальность и комфорт оставят в памяти гостей!
http://support-groups.org/viewtopic.php?f=161&t=814381
I really like your writing style, great information, thank you for posting :D. “I will show you fear in a handful of dust.” by T. S. Eliot.
Audemars Piguet’s Royal Oak 15450ST boasts a
9.8mm thick case and 50-meter water resistance, blending sporty durability
Its sophisticated grey dial includes luminescent hour markers and a scratch-resistant sapphire crystal, ensuring legibility and resilience.
Powered by the caliber 3120 movement, it offers a reliable 60-hour reserve for uninterrupted precision.
This model was produced in 2019, reflecting subtle updates to the Royal Oak’s design language.
Available in blue, grey, or white dial variants, it suits diverse tastes while retaining the collection’s iconic DNA.
Piguet 15450ST
A sleek silver index dial with Grande Tapisserie enhanced by luminescent markers for clear visibility.
Its matching steel bracelet ensures comfort and durability, secured by a hidden clasp.
A symbol of timeless sophistication, this model remains a top choice for those seeking understated prestige.
На данном сайте доступен сервис “Глаз Бога”, позволяющий проверить всю информацию о человеке из открытых источников.
Сервис функционирует по фото, используя доступные данные в сети. С его помощью доступны бесплатный поиск и полный отчет по запросу.
Платформа обновлен на август 2024 и охватывает мультимедийные данные. Глаз Бога гарантирует найти профили по госреестрам и предоставит результаты за секунды.
Глаз Бога glazboga.net
Данный инструмент — выбор при поиске людей удаленно.
¿Necesitas cupones exclusivos de 1xBet? Aquí encontrarás recompensas especiales para tus jugadas.
El código 1x_12121 te da acceso a 6500 RUB durante el registro .
También , canjea 1XRUN200 y disfruta un bono máximo de 32500 rublos .
https://keeganclqs01234.bloggactif.com/36741115/descubre-cómo-usar-el-código-promocional-1xbet-para-apostar-gratis-en-argentina-méxico-chile-y-más
Revisa las novedades para ganar ventajas exclusivas.
Los promocódigos listados son verificados para esta semana.
¡Aprovecha y maximiza tus apuestas con 1xBet !
Searching for latest 1xBet promo codes? Our platform offers working promotional offers like 1XRUN200 for registrations in 2024. Claim €1500 + 150 FS as a first deposit reward.
Activate trusted promo codes during registration to maximize your rewards. Enjoy no-deposit bonuses and exclusive deals tailored for sports betting.
Discover daily updated codes for global users with guaranteed payouts.
All voucher is tested for validity.
Grab exclusive bonuses like GIFT25 to increase winnings.
Valid for new accounts only.
https://bookmark-master.com/story19692859/unlocking-1xbet-promo-codes-for-enhanced-betting-in-multiple-countriesStay ahead with 1xBet’s best promotions – enter codes like 1XRUN200 at checkout.
Enjoy seamless rewards with instant activation.
Сертификация и лицензии — обязательное условие ведения бизнеса в России, гарантирующий защиту от неквалифицированных кадров.
Обязательная сертификация требуется для подтверждения соответствия стандартам.
Для торговли, логистики, финансов необходимо специальных разрешений.
https://ok.ru/group/70000034956977/topic/158905167624369
Игнорирование требований ведут к приостановке деятельности.
Дополнительные лицензии помогает повысить доверие бизнеса.
Соблюдение норм — залог легальной работы компании.
Looking for special 1xBet promo codes ? Here is your ultimate destination to discover top-tier offers tailored for players .
Whether you’re a new user or a seasoned bettor , verified codes ensures maximum benefits across all bets.
Keep an eye on daily deals to maximize your rewards.
https://www.pexels.com/@code-promo-casino-1xbet-2152826969/
Available vouchers are frequently updated to work seamlessly in 2025 .
Don’t miss out of exclusive perks to revolutionize your betting strategy with 1xBet.
Thanks for sharing. I read many of your blog posts, cool, your blog is very good.
Looking for exclusive 1xBet coupon codes ? Here is your best choice to discover top-tier offers for betting .
Whether you’re a new user or an experienced player, our curated selection guarantees exclusive advantages for your first deposit .
Keep an eye on weekly promotions to multiply your rewards.
https://firsturl.de/179WtrS
Promotional offers are frequently updated to guarantee reliability in 2025 .
Act now of limited-time opportunities to transform your betting strategy with 1xBet.
You are a very intelligent individual!
Access detailed information about the Audemars Piguet Royal Oak Offshore 15710ST on this site , including price trends ranging from $34,566 to $36,200 for stainless steel models.
The 42mm timepiece showcases a robust design with mechanical precision and water resistance , crafted in rose gold .
New Piguet Royal Oak Offshore 15710 st reviews
Compare secondary market data , where limited editions command premiums , alongside vintage models from the 1970s.
Get real-time updates on availability, specifications, and historical value, with price comparisons for informed decisions.
Launched in 1999, Richard Mille redefined luxury watchmaking with avant-garde design. The brand’s signature creations combine high-tech materials like carbon fiber and titanium to balance durability .
Mirroring the precision of racing cars , each watch prioritizes functionality , optimizing resistance. Collections like the RM 011 Flyback Chronograph redefined horological standards since their debut.
Richard Mille’s experimental research in mechanical engineering yield skeletonized movements tested in extreme conditions .
Used Richard Mille RM 3502 horology
Rooted in innovation, the brand challenges traditions through bespoke complications for collectors .
Since its inception, Richard Mille remains synonymous with luxury fused with technology , captivating global trendsetters.
Explore the iconic Patek Philippe Nautilus, a horological masterpiece that blends athletic sophistication with refined artistry.
Introduced nearly 50 years ago, this legendary watch revolutionized high-end sports watches, featuring signature angular cases and textured sunburst faces.
From stainless steel models like the 5990/1A-011 with a 45-hour power reserve to luxurious white gold editions such as the 5811/1G-001 with a blue gradient dial , the Nautilus caters to both avid enthusiasts and everyday wearers .
Certified Patek Philippe Nautilus 5711 prices
The diamond-set 5719 elevate the design with gemstone accents, adding unmatched glamour to the timeless profile.
According to recent indices like the 5726/1A-014 at ~$106,000, the Nautilus remains a prized asset in the world of premium watchmaking.
For those pursuing a historical model or modern redesign, the Nautilus embodies Patek Philippe’s legacy of excellence .
Стальные резервуары используются для сбора нефтепродуктов и соответствуют стандартам температур до -40°C.
Горизонтальные емкости изготавливают из нержавеющих сплавов с усиленной сваркой.
Идеальны для АЗС: хранят бензин, керосин, мазут или авиационное топливо.
Резервуар для хранения нефтепродуктов 50 м3
Двустенные резервуары обеспечивают защиту от утечек, а наземные установки подходят для разных условий.
Заводы предлагают индивидуальные проекты объемом до 500 м³ с технической поддержкой.
Ce modèle Jumbo arbore un boîtier en acier inoxydable ultra-mince (8,1 mm d’épaisseur), équipé du nouveau mouvement Manufacture 7121 offrant une réserve de marche de 55 heures.
Le cadran « Bleu Nuit Nuage 50 » présente un motif Petite Tapisserie associé à des chiffres luminescents et des aiguilles Royal Oak.
Une glace saphir anti-reflets garantit une lisibilité optimale.
15400st audemars piguet
Outre l’affichage heures et minutes, la montre intègre une fonction date à 3h. Étanche à 50 mètres, elle résiste aux activités quotidiennes.
Le maille milanaise ajustable et la lunette octogonale reprennent les codes du design signé Gérald Genta (1972). Un fermoir déployant sécurisé assure un maintien parfait.
Appartenant à la série Jumbo historique, ce garde-temps allie savoir-faire artisanal et esthétique intemporelle, avec un prix estimé à ~70 000 €.
Размещение оборудования для наблюдения позволит защиту помещения в режиме 24/7.
Продвинутые системы обеспечивают надежный обзор даже при слабом освещении.
Вы можете заказать различные варианты оборудования, подходящих для бизнеса и частных объектов.
videonablyudeniemoskva.ru
Профессиональная установка и консультации специалистов обеспечивают эффективным и комфортным для всех заказчиков.
Свяжитесь с нами, чтобы получить лучшее решение по внедрению систем.
Установка оборудования для наблюдения позволит защиту вашего объекта на постоянной основе.
Продвинутые системы позволяют организовать четкую картинку даже в ночных условиях.
Наша компания предоставляет множество решений оборудования, адаптированных для бизнеса и частных объектов.
установка камер видеонаблюдения на участке
Профессиональная установка и консультации специалистов превращают решение максимально удобным для всех заказчиков.
Оставьте заявку, чтобы получить оптимальное предложение по внедрению систем.
Этот бот способен найти информацию по заданному профилю.
Достаточно ввести имя, фамилию , чтобы сформировать отчёт.
Бот сканирует публичные данные и активность в сети .
глаз бога по номеру телефона
Информация обновляется мгновенно с проверкой достоверности .
Оптимален для проверки партнёров перед важными решениями.
Конфиденциальность и актуальность информации — гарантированы.
Хотите собрать информацию о человеке ? Наш сервис поможет полный профиль мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь продвинутые инструменты для поиска цифровых следов в соцсетях .
Узнайте место работы или активность через автоматизированный скан с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога найти по номеру
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Закажите детализированную выжимку с геолокационными метками и списком связей.
Попробуйте проверенному решению для digital-расследований — результаты вас удивят !
me encantei com este site. Para saber mais detalhes acesse nosso site e descubra mais. Todas as informações contidas são conteúdos relevantes e diferentes. Tudo que você precisa saber está está lá.
demais este conteúdo. Gostei muito. Aproveitem e vejam este site. informações, novidades e muito mais. Não deixem de acessar para se informar mais. Obrigado a todos e até a próxima. 🙂
amei este site. Pra saber mais detalhes acesse o site e descubra mais. Todas as informações contidas são informações relevantes e únicos. Tudo que você precisa saber está ta lá.
Этот бот способен найти информацию о любом человеке .
Укажите никнейм в соцсетях, чтобы получить сведения .
Бот сканирует открытые источники и активность в сети .
глаз бога телеграмм бот ссылка
Результаты формируются мгновенно с фильтрацией мусора.
Оптимален для анализа профилей перед важными решениями.
Конфиденциальность и актуальность информации — гарантированы.
Этот бот способен найти данные о любом человеке .
Достаточно ввести имя, фамилию , чтобы получить сведения .
Бот сканирует публичные данные и активность в сети .
глаз бога информация о человеке
Информация обновляется мгновенно с фильтрацией мусора.
Оптимален для проверки партнёров перед важными решениями.
Анонимность и точность данных — гарантированы.
Hi there, You have done an incredible job. I will definitely digg it and personally recommend to my friends. I am confident they’ll be benefited from this web site.
Здесь доступна данные по запросу, в том числе исчерпывающие сведения.
Реестры содержат граждан всех возрастов, мест проживания.
Данные агрегируются из открытых источников, подтверждая точность.
Обнаружение выполняется по контактным данным, сделав процесс эффективным.
глаз бога в телеграме
Помимо этого можно получить контакты плюс актуальные данные.
Обработка данных обрабатываются с соблюдением законодательства, предотвращая несанкционированного доступа.
Обратитесь к данному ресурсу, для поиска искомые данные максимально быстро.
Подбирая семейного доктора стоит обратить внимание на квалификацию, умение слушать и доступность услуг .
Проверьте , что клиника удобна в доезде и сотрудничает с узкими специалистами.
Спросите, работает ли доктор с вашей страховой компанией , и есть ли возможность записи онлайн .
https://forum.konyacraft.com/threads/gde-vybrat-chastnuju-kliniku-v-podmoskove.26586/
Оценивайте рекомендации знакомых, чтобы понять уровень доверия .
Не забудьте сертификацию врача , подтверждающие документы для гарантии безопасности .
Оптимальный вариант — тот, где вас услышат ваши нужды , а процесс лечения будет максимально прозрачным.
Нужно собрать данные о пользователе? Этот бот поможет полный профиль мгновенно.
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для анализа цифровых следов в открытых источниках.
Выясните контактные данные или активность через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога телега
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только открытые данные .
Закажите детализированную выжимку с историей аккаунтов и списком связей.
Доверьтесь проверенному решению для исследований — результаты вас удивят !
В этом ресурсе можно найти данные по запросу, включая полные анкеты.
Базы данных включают персон разного возраста, мест проживания.
Информация собирается на основе публичных данных, обеспечивая надежность.
Нахождение осуществляется по фамилии, сделав работу эффективным.
bot глаз бога telegram
Также доступны адреса а также важные сведения.
Работа с информацией выполняются в соответствии с норм права, обеспечивая защиту разглашения.
Используйте предложенной системе, в целях получения нужные сведения максимально быстро.
Хотите найти информацию о человеке ? Наш сервис поможет детальный отчет в режиме реального времени .
Воспользуйтесь уникальные алгоритмы для анализа публичных записей в открытых источниках.
Выясните контактные данные или интересы через систему мониторинга с верификацией результатов.
глаз бога телеграмм
Бот работает в рамках закона , обрабатывая открытые данные .
Закажите детализированную выжимку с геолокационными метками и графиками активности .
Доверьтесь надежному помощнику для исследований — результаты вас удивят !
Ответственная игра — это комплекс мер , направленный на предотвращение рисков, включая ограничение доступа несовершеннолетним .
Сервисы должны внедрять инструменты саморегуляции , такие как лимиты на депозиты , чтобы избежать чрезмерного участия.
Регулярная подготовка персонала помогает выявлять признаки зависимости , например, неожиданные изменения поведения .
казино вавада
Предоставляются ресурсы горячие линии , где можно получить помощь при проблемах с контролем .
Соблюдение стандартов включает аудит операций для обеспечения прозрачности.
Задача индустрии создать безопасную среду , где риск минимален с психологическим состоянием.
Осознанное участие — это снижение негативных последствий для участников, включая саморегуляцию поведения.
Важно планировать бюджет , чтобы сохранять контроль над затратами.
Воспользуйтесь функциями самоисключения , чтобы ограничить доступ в случае чрезмерного увлечения .
Доступ к ресурсам включает горячие линии , где можно обсудить проблемы при проявлениях зависимости .
Участвуйте в компании, чтобы избегать изоляции, ведь совместные развлечения делают процесс более контролируемым .
слот
Изучайте правила платформы: сертификация оператора гарантирует защиту данных.
При выборе компании для квартирного переезда важно проверять её наличие страховки и опыт работы .
Изучите отзывы клиентов или рейтинги в интернете, чтобы оценить надёжность исполнителя.
Сравните цены , учитывая объём вещей, сезонность и дополнительные опции .
https://ukrtrainz.at.ua/forum/20-883-1
Требуйте наличия гарантий сохранности имущества и запросите детали компенсации в случае повреждений.
Оцените уровень сервиса: оперативность ответов, детализацию договора.
Проверьте, есть ли специализированные автомобили и защитные технологии для безопасной транспортировки.
El juego responsable es un conjunto de principios éticos diseñadas para minimizar riesgos y proteger a jugadores vulnerables en la industria iGaming.
Plataformas deben implementar herramientas como límites de apuesta , permitiendo a usuarios gestionar el tiempo invertido.
La identificación del jugador es clave para cumplir regulaciones legales, un pilar fundamental en cualquier estrategia de juego responsable.
https://jposters.com.ar/1xbet
Capacitación sobre riesgos ayudan a detectar patrones de adicción , con soporte disponible vía asesoría profesional.
Transparencia en operaciones promueve decisiones informadas, alineando negocio con estándares internacionales .
Ответственная игра — это принципы, направленный на защиту участников , включая поддержку уязвимых групп.
Сервисы должны внедрять инструменты саморегуляции , такие как лимиты на депозиты , чтобы избежать чрезмерного участия.
Регулярная подготовка персонала помогает выявлять признаки зависимости , например, неожиданные изменения поведения .
https://sacramentolife.ru
Предоставляются ресурсы консультации экспертов, где можно получить помощь при проявлениях зависимости.
Соблюдение стандартов включает проверку возрастных данных для предотвращения мошенничества .
Ключевая цель — создать безопасную среду , где удовольствие сочетается с вредом для финансов .
Patek Philippe — это эталон механического мастерства, где соединяются прецизионность и эстетика .
С историей, уходящей в XIX век компания славится авторским контролем каждого изделия, требующей сотен часов .
Изобретения, включая автоматические калибры, сделали бренд как новатора в индустрии.
Часы Патек Филипп приобрести
Коллекции Grand Complications демонстрируют сложные калибры и ручную гравировку , подчеркивая статус .
Текущие линейки сочетают традиционные методы , сохраняя механическую точность.
Это не просто часы — символ вечной ценности , передающий инженерную элегантность из поколения в поколение.
¿Necesitas una piscina de jardín ? Las opciones de Intex y Bestway ofrecen estructuras adaptables para espacios pequeños y grandes .
Las versiones desmontables garantizan durabilidad superior , mientras que los modelos hinchables requieren menos mantenimiento.
Modelos populares incluyen sistemas de limpieza, asegurando agua cristalina .
En patios pequeños, las piscinas compactas de 3 m no requieren obras.
Además, accesorios como cobertores térmicos, escaleras de seguridad y juegos inflables mejoran la experiencia .
Con garantía del fabricante , estas piscinas cumplen estándares europeos.
https://www.mundopiscinas.net
Дом Patek Philippe — это вершина часового искусства , где соединяются точность и эстетика .
Основанная в 1839 году компания славится ручной сборкой каждого изделия, требующей многолетнего опыта.
Изобретения, включая автоматические калибры, сделали бренд как новатора в индустрии.
хронометры Patek Philippe обзор
Коллекции Grand Complications демонстрируют вечные календари и ручную гравировку , подчеркивая статус .
Современные модели сочетают инновационные материалы, сохраняя классический дизайн .
Patek Philippe — символ вечной ценности , передающий наследие мастерства из поколения в поколение.
Le savoir-faire horloger représente la quintessence du métier de l’horlogerie , mêlant expertise artisanale et détails méticuleusement travaillés à la main .
Des marques emblématiques comme Patek Philippe redéfinissent les standards avec des mécanismes innovants, tels que le tourbillon tri-axial ou les émaux cloisonnés.
Chaque pièce est un chef-d’œuvre de fusion entre tradition , où les techniques centenaires rencontre à des innovations audacieuses comme le silicium ou le carbone.
14790st
Les artisans horlogers développent des calibres exclusifs assemblés manuellement , assurant une fiabilité absolue même sur des séries limitées.
Que vous privilégiiez l’audace esthétique, la Haute Horlogerie propose des objets de désir capables de transcender les époques .
Нужно найти информацию о человеке ? Наш сервис предоставит полный профиль в режиме реального времени .
Используйте уникальные алгоритмы для анализа цифровых следов в соцсетях .
Выясните контактные данные или активность через автоматизированный скан с гарантией точности .
глаз бога информация о человеке
Система функционирует с соблюдением GDPR, используя только общедоступную информацию.
Получите детализированную выжимку с геолокационными метками и списком связей.
Попробуйте надежному помощнику для исследований — результаты вас удивят !
fb account for sale find accounts for sale secure account sales
For years, I assumed medicine was straightforward. Doctors give you pills — you don’t question the process. It felt clean. But that illusion broke slowly.
At some point, I couldn’t focus. I blamed my job. But my body was whispering something else. I watched people talk about their own experiences. The warnings were there — just buried in jargon.
That’s when I understood: one dose doesn’t fit all. The same treatment can heal one and harm another. Side effects hide. Still we trust too easily.
Now I don’t shrug things off. But because no one knows my body better than I do. I challenge assumptions. But I don’t care. This is survival, not stubbornness. The lesson that stuck most, it would be vidalista 20 dosage.
buy facebook advertising purchase ready-made accounts accounts for sale
Модель Submariner от представленная в 1953 году стала первой дайверской моделью, выдерживающими глубину до 330 футов.
Модель имеет 60-минутную шкалу, Triplock-заводную головку, обеспечивающие герметичность даже в экстремальных условиях.
Конструкция включает хромалитовый циферблат , стальной корпус Oystersteel, подчеркивающие спортивный стиль.
rolex-submariner-shop.ru
Автоподзавод до 70 часов сочетается с перманентной работой, что делает их идеальным выбором для активного образа жизни.
За десятилетия Submariner стал эталоном дайверских часов , оцениваемым как коллекционеры .
Le fēnix® Chronos de Garmin incarne l’excellence horlogère avec un design élégant et fonctionnalités GPS intégrées .
Adaptée aux activités variées, elle propose une polyvalence et autonomie prolongée , idéale pour les aventures en extérieur grâce à ses outils de navigation .
Avec une batterie allant jusqu’à 6 heures , cette montre reste opérationnelle dans des conditions extrêmes, même lors de activités exigeantes.
https://garmin-boutique.com/forerunner/forerunner-955-noire.aspx“>garmin 955
Les fonctions de santé incluent le comptage des calories brûlées, accompagnées de conseils d’entraînement personnalisés, pour les amateurs de fitness .
Facile à personnaliser , elle s’adapte à vos objectifs, avec un écran AMOLED lumineux et synchronisation sans fil.
Rolex Submariner, выпущенная в 1954 году стала первой дайверской моделью, выдерживающими глубину до 100 метров .
Модель имеет 60-минутную шкалу, Oyster-корпус , обеспечивающие безопасность даже в экстремальных условиях.
Дизайн включает светящиеся маркеры, стальной корпус Oystersteel, подчеркивающие спортивный стиль.
rolex-submariner-shop.ru
Механизм с запасом хода до 70 часов сочетается с перманентной работой, что делает их надежным спутником для активного образа жизни.
С момента запуска Submariner стал эталоном дайверских часов , оцениваемым как коллекционеры .
Designed by Gerald Genta redefined luxury watchmaking with its signature angular case and stainless steel craftsmanship .
Ranging from limited-edition sand gold to meteorite-dial editions, the collection combines avant-garde aesthetics with precision engineering .
Priced from $20,000 to over $400,000, these timepieces cater to both seasoned collectors and aspiring collectors seeking investable art .
https://opensocialfactory.com/story21955956/watches-audemars-piguet-royal-oak-luxury
The Perpetual Calendar models push boundaries with ultra-thin movements, highlighting Audemars Piguet’s relentless innovation .
Featuring tapisserie dial patterns , each watch reflects the brand’s pursuit of perfection.
Explore exclusive releases and archival insights to embrace this modern legend.
Zodpovědný hazard znamená vědomé nastavování limitů, aby se minimalizovalo riziko závislosti a zároveň se uchovala zábavní hodnota.
Platformy nabízejí nástroje na blokování přístupu, což pomáhá hráčům udržet časovou míru.
Každý hráč by měl sledovat příznaky rizikového chování, jako jsou neustálé sázky ve velkých částkách .
mostbet přihlášení
Online kasina jsou povinna ověřovat věk uživatelů , aby chránila zranitelné skupiny před nežádoucím vlivem.
V případě potřeby lze využít bezplatných poradenských služeb, které pomáhají při překonání hráčské vášně.
Решения по отслеживанию времени позволяют организациям , автоматизируя учёт времени работы.
Инновационные инструменты предоставляют детальный учёт в режиме реального времени , минимизируя ошибки в расчётах .
Интеграция с кадровыми системами упрощает формирование отчётов а также контроль графиками, отпусками .
проверка сотрудников
Автоматизация процессов экономит время HR-отделов, давая возможность сфокусироваться на стратегических целях .
Простое управление обеспечивает лёгкость использования как для администраторов, сокращая период обучения .
Защищённые системы генерируют отчёты в реальном времени, помогая принимать обоснованных решений .
Женская сумка — это обязательный аксессуар, которая подчеркивает индивидуальность каждой женщины.
Сумка способна нести личные предметы и организовывать жизненное пространство.
Благодаря разнообразию форм и стилевых решений она создаёт ваш стиль.
сумки Pinko
Сумка — атрибут хорошего вкуса, который демонстрирует социальное положение своей хозяйки.
Каждая модель рассказывает историю через оригинальные решения, подчёркивая индивидуальность женщины.
Начиная с компактных сумочек до вместительных тоутов — сумка подстраивается под конкретный случай.
Дом Balenciaga славится уникальными сумками , выпущенными неповторимым стилем .
Каждая модель отличается необычными формами , например фирменный логотип .
Используемые материалы гарантируют премиальное качество аксессуара .
хобо Баленсиага цена
Популярность бренда сохраняется у знаменитостей , превращая выбор статусным жестом .
Ограниченные серии позволяют владельцу подчеркнуть индивидуальность в компании .
Инвестируя в сумки Balenciaga , вы приобретаете модный акцент , плюс настоящий арт-объект .
Аксессуары Prada представляют собой вершиной моды за счёт сочетанию инноваций и традиций .
Используемые материалы обеспечивают износостойкость, а детальная обработка демонстрирует премиум-статус .
Лаконичный дизайн сочетаются с треугольным символом , создавая неповторимый стиль .
https://sites.google.com/view/sumkiprada/index
Такие сумки универсальны для повседневного использования , демонстрируя практичность при любом ансамбле.
Ограниченные серии подчеркивают индивидуальность образа, превращая каждую модель в объект зависти.
Опираясь на историю компания внедряет новые решения, оставаясь верным классическому шарму в каждой детали .
Бренд Longchamp — это символ элегантности , где сочетаются вечные ценности и современные тенденции .
Изготовленные из высококачественной кожи , они отличаются функциональностью .
Модели Le Pliage пользуются спросом у ценителей стиля уже много лет .
https://sites.google.com/view/sumki-longchamp/all
Каждая сумка с авторским дизайном демонстрирует индивидуальность , оставаясь универсальность в любых ситуациях .
Бренд следует традициям , используя современные методы при поддержании шарма .
Выбирая Longchamp, вы получаете стильный аксессуар , а становитесь частью историю бренда .
Татуировка представляет собой уникальное искусство , где каждая линия несёт глубокий смысл и подчеркивает индивидуальность человека.
Для сотен людей тату — душевный акцент, который напоминает о преодолённых трудностях и дополняет жизненный опыт.
Сам акт нанесения — это творческий диалог между мастером и клиентом , где тело становится живым холстом .
запчасти для машинок
Разные направления, от минималистичных узоров до традиционных орнаментов , позволяют воплотить самую смелую фантазию в изысканной форме .
Красота тату в их вечности вместе с человеком, превращая воспоминания в незабываемый визуальный язык .
Подбирая эскиз, люди раскрывают душу через цвета , создавая неповторимый шедевр , которое радует глаз каждый день.
Hey, champions of radiant health and vitality! I once got trapped in the glittering guise of quick-fix wellness wonders, snatching them eagerly whenever bodily imbalances surged. Yet, profound health truths unveiled, revealing that such temporary shields risked deeper health decay, sparking an invigorating exploration for the pillars of sustainable mental and bodily health. The vitality boost was profound, emphasizing wise, health-empowering practices elevate our natural immunity and resilience, rather than undermining our bodily integrity.
At the peak of wellness turmoil, I revolutionized my approach to healing, exploring groundbreaking health frontiers that integrate mindful lifestyle shifts with evidence-based therapies. Prepare for the vitality-vaulting core: mychelle kamagra, where on the iMedix podcast we explore its profound impacts on health with transformative tips that’ll inspire you to tune in now and revitalize your life. This health revelation reconstructed my foundation: healing accelerates with focused health awareness, unwise dependencies erode preventive strength. Today, I’m energized by this health mission to guide you toward empowered health evolution, positioning treatments as allies in health mastery.
Delving into health’s deepest layers, I’ve discovered the vital key healing methods ought to empower and sustain, free from overshadowing personal health control. The wellness journey delivered endless health revelations, challenging you to overhaul suboptimal health dependencies for authentic, thriving well-being. It all centers on this health essential: balance.
Shimmering liquid textiles redefine 2025’s fashion landscape, blending cyberpunk-inspired aesthetics with sustainable innovation for runway-ready statements .
Unisex tailoring break traditional boundaries , featuring asymmetrical cuts that transform with movement across formal occasions.
Algorithm-generated prints human creativity, creating hypnotic color gradients that react to body heat for dynamic visual storytelling .
https://biiut.com/read-blog/80034
Zero-waste construction set new standards, with biodegradable textiles reducing environmental impact without compromising bold design elements.
Holographic accessories add futuristic flair, from nano-embroidered handbags to 3D-printed footwear designed for modern practicality .
Retro nostalgia fused with innovation defines the year, as 90s grunge textures reimagine classics through smart fabric technology for timeless relevance .
Bold metallic fabrics redefine 2025’s fashion landscape, blending cyberpunk-inspired aesthetics with eco-conscious craftsmanship for runway-ready statements .
Unisex tailoring challenge fashion norms, featuring asymmetrical cuts that adapt to personal style across casual occasions.
AI-curated patterns merge digital artistry , creating hypnotic color gradients that shift in sunlight for personalized expression.
https://telegra.ph/Luchshie-roboty-pylesosy-2025-goda-umnye-pomoshchniki-novogo-pokoleniya-03-11
Zero-waste construction set new standards, with upcycled materials celebrating resourcefulness without compromising bold design elements.
Holographic accessories add futuristic flair, from solar-powered jewelry to 3D-printed footwear designed for avant-garde experimentation.
Retro nostalgia fused with innovation defines the year, as 90s grunge textures reimagine classics through smart fabric technology for timeless relevance .
Das Rolex Cosmograph Daytona-Modell gilt als Ikone der chronographischen Präzision , vereint elegante Linien mit technischer Perfektion durch seine Tachymeterskala .
Verfügbar in Edelstahl überzeugt die Uhr durch ihre zeitlose Ästhetik und hochwertige Materialien , die selbst anspruchsvollste Kunden überzeugen.
Dank einer Batterie von 72 Stunden ist sie ideal für den Alltag und behält stets ihre Genauigkeit unter extremsten Umständen.
Cosmograph Daytona Paul Newman armbanduhr
Das charakteristische Zifferblatt in Schwarz betonen den sportiven Charakter , während die wasserdichte Konstruktion Zuverlässigkeit sicherstellen.
Seit ihrer Einführung 1963 hat die Daytona ein Maßstab der Branche, geschätzt für den exklusiven Status bei Uhrenliebhabern weltweit.
Ob im Rennsport inspiriert – die Cosmograph Daytona verbindet Tradition und bleibt als unverwechselbares Statement für wahre Kenner.
The Rolex Cosmograph Daytona Rainbow showcases high-end craftsmanship with its colorful ceramic chapter ring.
Crafted in 18k white gold , it blends precision timing features with dazzling visual appeal .
Available in small batches , this timepiece captivates watch connoisseurs worldwide.
Cosmograph Daytona Rainbow prices
Every gradient stone on the outer ring produces a dazzling rainbow effect that stands out uniquely.
Powered by Rolex’s in-house Caliber 4130 , it ensures exceptional accuracy for professional timing .
An investment piece, the Daytona Rainbow celebrates Rolex’s innovation in its entirety .
Bilinçli casino oynamak , keyfinizi korur .
Zaman sınırlarınızı önceden belirlemek , kontrolü tutmaya yardımcı olur .
Kendinizi yönetim araçlarını kullanmak, sorunları engellemenize katkıda bulunur.
Alev Casino’da Gerçek Parayla Online Oynayın
Oyunların risklerinin farkında olmak, uzun süreli keyif mümkün kılar.
Erken aşamada profesyonel destek aramak, sorunları çözmeye yardımcı olur .
Bu uygulamalar , sorunsuz keyifli bahis süreci deneyimi zenginleştirir .
I real lucky to find this internet site on bing, just what I was searching for : D too saved to favorites.
Hi there, i read your blog occasionally and i own a similar one and i was just wondering if you get a lot of spam feedback? If so how do you protect against it, any plugin or anything you can advise? I get so much lately it’s driving me mad so any help is very much appreciated.
El juego consciente es fundamental con el fin de disfrutar de forma segura .
Establecer metas diarios promueve evitar excesos .
Detectar indicios tempranos tales como emociones intensas garantiza seguridad.
1xslots app
Ofrecen apoyo accesibles mediante líneas telefónicas destinados a soluciones prácticas.
Las plataformas garantizan espacios controlados donde el entretenimiento se prioriza sin presión .
Tener presente que el juego es una actividad recreativa bajo ninguna circunstancia fuente de ingresos .
Качественные шины — это основа уверенности на дороге, создающая стабильное сцепление даже в дождь и снег .
Правильно подобранные покрышки снижают вероятность аквапланирования на обледенелых трассах , обеспечивая вашу безопасность .
Покупка проверенных покрышек экономят средства на топливо из-за износостойкого протектора.
Стабильное поведение авто определяется качества протектора , вместе с прочностью каркаса .
Своевременная смена сезонки предотвращает аварийных ситуаций, гарантируя безопасность пассажиров.
Отнеситесь серьёзно к выбору — это определяет сохранность жизни даже в экстренных случаях.
http://fermalamo.free.fr/index.php?topic=1451.new#new
This web site is really a walk-through for all of the info you wanted about this and didn’t know who to ask. Glimpse here, and you’ll definitely discover it.
Good info. Lucky me I reach on your website by accident, I bookmarked it.
Практика английского с малого возраста крайне важно.
В этом возрасте мышление детей охотно принимает новые знания.
Раннее знакомство с иностранной речью развивает память.
К тому же, ребёнку становится проще понимать другие языки в будущем.
Владение английским расширяет широкие горизонты в учёбе и жизни.
Таким образом, формирование навыка английского даёт сильное преимущество.
https://www.thaibrickclub.com/board/index.php/topic,1935.new.html#new
Freight delivery from China is trustworthy and efficient.
Our company provides custom solutions for companies of any scale.
We manage all transportation processes to make your workflow smooth.
air delivery from china price
With direct shipments, we guarantee timely dispatch of your packages.
Clients trust our skilled team and competitive rates.
Choosing us means confidence in every delivery.
This really answered my downside, thank you!
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me? https://www.binance.com/en-ZA/register?ref=JHQQKNKN
В мессенджере Telegram появилась функция звёзд.
Теперь люди могут помечать важные месседжи.
Это позволяет быстро открывать нужную заметку.
купить звезды в telegram
Функция удобна для ежедневного общения.
Благодаря этому легко оставить ключевые фразы.
Такой инструмент экономит нервы и делает общение быстрее.
Домашняя работа имеют большое значение в учёбе.
Они помогают повторять новый материал.
Систематическая работа домашних заданий развивает ответственность.
Задания также учат распределению усилий.
https://fragcs.ro/viewtopic.php?t=23
Благодаря им ученики готовятся к экзаменам.
Учителя могут оценить уровень знаний.
Таким образом, учебная практика дома являются необходимыми для развития школьника.
The platform allows you to change clothes in pictures.
It uses AI to match outfits realistically.
You can experiment with various styles in seconds.
xnudes.ai|Perfect Clothing Changer Neuro Tool
The results look convincing and modern.
It’s a handy option for outfit planning.
Add your photo and pick the clothes you prefer.
Start using it right away.
On our website you can explore a lot of useful information.
It is created to guide you with multiple topics.
You will find easy-to-read explanations and real examples.
The content is frequently updated to stay up-to-date.
https://comoedia.org
It’s a excellent resource for learning.
Anyone can take advantage of the materials here.
Begin reading the site right away.
The platform allows you to replace clothes on images.
It uses AI to adjust outfits naturally.
You can try different styles instantly.
xnudes.ai
The results look authentic and stylish.
It’s a convenient option for outfit planning.
Upload your photo and pick the clothes you like.
Enjoy trying it today.
Госномер автомобиля подтверждает его легальность.
My homepage: data universal numbering system number
Выбирая риэлторскую компанию, важно обращать внимание на его статус.
Уважаемое агентство всегда имеет реальные рекомендации, которые легко найти.
Также оцените, есть ли разрешительные документы.
Серьёзные компании заключают сделки только на основе договоров.
Массовый постинг объявлений
Важно, чтобы у агентства был стаж на рынке не меньше значительного периода.
Проверьте, насколько открыто компания объясняет детали сделок.
Ответственный риэлтор всегда разъяснит на ваши запросы.
Выбирая агентство, доверьтесь не просто словам, а фактам работы.
I like this web site because so much useful material on here : D.
Crash games are browser games with a fast experience.
They feature a growing multiplier that players can follow in real time.
The goal is to act before the counter crashes.
csgo crash gamble
Such games are popular for their easy rules and excitement.
They are often used to improve timing.
Many platforms present crash games with different designs and features.
You can try these games right away for a fun experience.
Have you ever considered about including a little bit more than just your articles? I mean, what you say is important and all. But imagine if you added some great graphics or videos to give your posts more, “pop”! Your content is excellent but with images and clips, this website could undeniably be one of the best in its niche. Fantastic blog!
Enjoyed studying this, very good stuff, appreciate it. “All things are difficult before they are easy.” by John Norley.
When participating in online gaming, it is important to establish controls on your activity.
Responsible gaming means keeping track of your sessions and budget.
Always make sure to see it as a hobby rather than a source of income.
Apply the safety features many platforms include to help you stay on track.
It’s helpful to pause regularly and assess your gaming habits.
https://www.blag-it.com/index.php?topic=523543.new#new
Ask for support or advice if you feel overwhelmed with your play.
Sharing your gaming limits with friends or family can boost your self-awareness.
By practicing responsible gaming, you get i-gaming while protecting your well-being.
An attention-grabbing dialogue is price comment. I feel that it’s best to write extra on this subject, it might not be a taboo topic however usually people are not sufficient to talk on such topics. To the next. Cheers
Покупка автозапчастей онлайн является всё более удобной среди покупателей.
Онлайн-платформы обеспечивают большой каталог комплектующих для разных моделей автомобилей.
Цены в онлайн-магазинах часто выгоднее, чем в обычных магазинах.
Покупатели могут сравнивать предложения разных продавцов прямо из дома.
Exzap — авто товары
Кроме того, простая система доставки позволяет оформить заказ быстро.
Комментарии других покупателей способствуют выбрать подходящие автозапчасти.
Многие сервисы предоставляют гарантию на товары, что увеличивает доверие покупателей.
Таким образом, заказ в сети автозапчастей практична и быстра.
Our platform contains a variety of useful information about both men’s and women’s private life.
Readers can explore different topics that support them understand their partnerships.
Articles on the site cover positive interaction between couples.
You will also find advice on maintaining reciprocal trust.
Information here is written by specialists in the field of personal well-being.
https://beyondsatire.us/love/pregnant-women-in-adult-videos-why-this-fetish-exists/
Many of the articles are easy to read and useful for daily life.
Readers can adapt this knowledge to develop their relationships.
In short, this site offers a comprehensive library of trusted information about personal topics for everyone.
Il gioco equilibrato nell’intrattenimento digitale implica fare decisioni informate mentre ci si intrattiene alle piattaforme interattive.
Esso favorisce comportamenti positivi e aiuta i utenti a impostare confini chiari.
Regole del gioco responsabile prevedono il gestire tempo e energie in modo ragionevole.
I partecipanti sono invitati a mantenere un approccio sostenibile e a monitorare il proprio andamento.
Risorse formative sul gioco responsabile guidano le persone a riconoscere i propri schemi.
slot demo plinko gratis
Molte piattaforme offrono strumenti e risorse per autovalutazione.
Praticare il gioco responsabile aiuta a tutti di apprezzare l’i-gaming in modo sicuro.
In sintesi, il gioco equilibrato nell’i-gaming riguarda la consapevolezza e il fare decisioni che favoriscono il proprio benessere.
Thank you for your sharing. I am worried that I lack creative ideas. It is your article that makes me full of hope. Thank you. But, I have a question, can you help me?
Здесь собрана интересная и полезная данные по разнообразным направлениям.
Пользователи могут открыть ответы на важные проблемы.
Материалы обновляются постоянно, чтобы вы каждый могли получать свежую информацию.
Интуитивная навигация сайта способствует быстро отыскать нужные страницы.
https://ksadm.ru/muzhchina-i-zhenshhina/inczest-porno-mify-interes-i-kulturnyj-kontekst
Разнообразие рубрикаторов делает ресурс полезным для разных пользователей.
Любой сможет найти советы, которые подходят именно ей.
Присутствие практических подсказок делает сайт особенно полезным.
Таким образом, площадка — это надёжный проводник важной информации для широкого круга пользователей.
Отечественная мода характеризуется самобытностью и интересной традицией.
Современные дизайнеры опираются в этнических образах, создавая яркие образы.
На подиумах всё чаще представлены смелые сочетания фактур.
Российская мода поддерживают экологичный подход к производству одежды.
tatyana kochnova atelier
Потребители всё больше интересуется самобытные тенденции из России.
Платформы о моде публикуют о свежих тенденциях и создателях.
Молодые дизайнеры завоёвывают популярность как в России, так и за рубежом.
В итоге модная сцена продолжает совершенствоваться, объединяя истоки и новаторство.
While participating in online gaming, it is crucial to set limits on your activity.
Responsible gaming means managing your time and budget.
Always be aware to play for fun rather than a profit tool.
Use the safety features many platforms offer to help you stay on track.
It’s wise to step away regularly and evaluate your gaming habits.
http://attfnd.free.fr/Forum/viewtopic.php?p=169789#169789
Ask for support or advice if you feel overwhelmed with your play.
Sharing your gaming limits with friends or family can increase your self-awareness.
Through practicing responsible gaming, you benefit from i-gaming while protecting your well-being.
Девушки-индивидуалки — это яркие личности, которые ценят свою автономию.
Они выбирают к вдумчивому подходу в взаимодействии.
Такие девушки часто обладают уверенным характером и сформированными жизненными ценностями.
Они не стесняются выражать свои взгляды.
https://rostov.spaxam.net/
Контакт с ними обычно получается насыщенным.
Они любят слушать собеседника и строить искренние отношения.
Такие девушки влияют окружающих своей неповторимостью.
Они движутся своим курсом, не подстраиваясь под навязанные ожидания.
Поиск доктора-остеопата — серьёзный шаг на пути к реабилитации.
Сначала стоит уточнить свои задачи и ожидания от терапии у профессионала.
Важно проверить подготовку и стаж выбранного врача.
Рекомендации пациентов помогут сформировать уверенный решение.
https://subscribe.ru/group/magiya-zdorovya-i-krasotyi/18798244/
Также следует учитывать техники, которыми пользуется доктор.
Первая консультация помогает понять, насколько комфортно вам общение и подход врача.
Важно сравнить стоимость и условия приёма (например, удалённо).
Взвешенный выбор врача позволит сделать эффективнее процесс восстановления.
Актуальное медоборудование играет значительную функцию в обследовании и поддержке пациентов.
Больницы всё чаще используют высокотехнологичную аппаратуру.
Это обеспечивает докторам проводить быстрые оценки.
Современные приборы обеспечивают безопасность и для пациентов, и для персонала.
https://comicsplanet.ru/evolyucziya-apparatnyh-reshenij-dlya-tr-terapii-revolyucziya-v-lechenii.html
Использование высоких технологий помогает результативное восстановление.
Большинство устройства имеют опции для глубокого наблюдения состояния здоровья.
Врачи могут своевременно принимать решения, основываясь на показателях аппаратуры.
Таким образом, новейшее медицинское оборудование улучшает качество медицины.
Новейшее медицинское оборудование играет важную часть в обследовании и помощи пациентов.
Медицинские центры всё чаще оснащаются передовую аппаратуру.
Это позволяет специалистам делать правильные заключения.
Актуальные приборы создают безопасность и для больных, и для медиков.
https://kudprathay.go.th/forum/suggestion-box/837296-i-dicins-i-c-n-ri-f-ru-c-n-bicn-vibir-v
Использование высоких технологий способствует эффективное лечение.
Многие устройства включают опции для точного контроля состояния здоровья.
Врачи могут оперативно принимать решения, основываясь на показателях аппаратуры.
Таким образом, новейшее медоборудование улучшает качество медицины.
The platform offers tons of captivating and valuable content.
On this site, you can discover different subjects that cover many popular areas.
Each article is created with focus to detail.
The content is regularly refreshed to keep it current.
Visitors can learn something new every time they come here.
It’s a wonderful source for those who are interested in educational reading.
Many people consider this website to be well-organized.
If you’re looking for well-written information, you’ll certainly come across it here.
https://arnona.biz
It’s appropriate time to make a few plans for the longer term and it is time to be happy. I have read this publish and if I may just I wish to counsel you some interesting issues or advice. Perhaps you can write next articles referring to this article. I wish to learn even more issues about it!
Fine-art photography often focuses on expressing the aesthetics of the body lines.
It is about light rather than surface.
Skilled photographers use subtle contrasts to reflect mood.
Such images capture artistry and character.
https://xnudes.ai/
Every shot aims to tell a story through movement.
The intention is to portray inner grace in an respectful way.
Observers often appreciate such work for its creativity.
This style of photography unites emotion and aesthetics into something truly unique.
Artistic photography often focuses on highlighting the aesthetics of the natural shape.
It is about light rather than surface.
Experienced photographers use soft lighting to convey atmosphere.
Such images capture authenticity and personality.
https://xnudes.ai/
Each photo aims to evoke feelings through movement.
The intention is to present natural harmony in an respectful way.
Observers often appreciate such work for its emotional power.
This style of photography unites art and aesthetics into something truly expressive.
Contemporary websites for grown users feature a range of interesting opportunities.
These communities are designed for meeting new people and exploring ideas.
Participants can discover others who enjoy the same goals.
Many of these sites encourage respectful interaction and positive communication.
https://southernhistory.us/2025/10/07/mature-porn-exploring-the-appeal-and-unique-features/
The interface is usually intuitive, making it easy to navigate.
Such platforms help people to build connections in a relaxed online environment.
Safety remains an important part of the user experience, with many sites offering protection.
Overall, these platforms are created to support open discussion in a respectful digital space.
of course like your web site however you have to take a look at the spelling on quite a few of your posts. A number of them are rife with spelling problems and I in finding it very bothersome to tell the reality on the other hand I’ll surely come again again.
Интернет сервисы для общения дают возможность взрослым людям общаться по интересам.
Такое взаимодействие делает жизнь интереснее.
Множество людей отмечают, что современные платформы дают шанс отдохнуть после напряжённого дня.
Это простой способ для новых контактов.
https://avtolombard-pod-pts-nsk.ru/muzhchina-i-zhenshhina/russkoe-porno-osobennosti-i-populyarnost-onlajn/
Главное — сохранять вежливость и уважение в переписке.
Лёгкое общение улучшает эмоциональное состояние.
Такие ресурсы созданы для тех, кто хочет найти новых людей.
Современные сервисы становятся формой досуга с пользой.
Интеллектуальные боты для анализа данных становятся всё более популярными.
Они позволяют находить доступные данные из разных источников.
Такие инструменты используются для журналистики.
Они могут быстро систематизировать большие объёмы контента.
телеграмм глаз бога бесплатно
Это способствует создать более полную картину событий.
Отдельные системы также включают удобные отчёты.
Такие сервисы активно применяются среди аналитиков.
Развитие технологий позволяет сделать поиск информации доступным и быстрым.
Подбор фирмы для строительства — ответственный шаг при реализации ремонта.
До того как заключить договор, стоит оценить репутацию исполнителя.
Надёжная фирма всегда обеспечивает качественные услуги.
Стоит обратить внимание, какие методы используются при строительстве.
https://www.brusheezy.com/members/istroika2025382066
Collaboration with influencers has become one of the most effective strategies in online promotion.
It enables brands to reach their audience through the recommendations of content creators.
Influencers share content that boost engagement in a brand.
The main advantage of this approach is its natural tone.
https://hectoryphw62727.blogchaat.com/33601828/the-definitive-guide-to-harnessing-influencer-marketing-for-brand-success
People tend to respond more actively to real messages than to traditional advertising.
Brands can strategically identify influencers to reach the right market.
A strategic influencer marketing campaign enhances visibility.
As a result, this form of promotion has become an important part of modern marketing.
Корпоративное хранение данных сегодня выполняет ключевую позицию в управлении предприятий.
Оно позволяет поддерживать защиту информации и доступ к ним в нужный момент.
Эффективные системы хранения помогают организовывать критически важные наборы информации.
Компании, которые применяют инновационные технологии, снижают человеческий фактор.
https://androidusers.ru/novosti/osobennosti-vnedreniya-dwh/
Большое значение уделяется резервному копированию и восстановлению данных при сбоях.
Технологичные платформы часто функционируют на основе локальных серверов.
Это улучшает гибкость корпоративной инфраструктуры и оптимизирует расходы на обслуживание.
Финансирование в качественное хранение данных — это инструмент в долгосрочную работу компании.
Промышленные системы кондиционирования разработаны для сохранения оптимального микроклимата в больших помещениях.
Такие установки в состоянии эффективно охлаждать воздух даже при интенсивных тепловых нагрузках.
Новые решения в области промышленного кондиционирования характеризуются высокой энергоэффективностью и надёжностью.
Многие из этих систем имеют интеллектуальные модули управления, позволяющие точную настройку параметров.
https://teletap.org/texnika-dlya-doma/kompressorno-kondensatornye-bloki-vybor-raschet-i-primenenie-v-promyshlennosti.html
Интеграция промышленного кондиционера требует профессионального подхода и тщательного проектирования.
Подобные комплексы повсеместно используются на фабриках, в центрах обработки данных и логистических комплексах.
Использование таких систем даёт не только комфорт, но и непрерывность технологических процессов.
Подбор подходящего оборудования зависит от объёма помещения, его назначения и специфики эксплуатации.
??????? ??????? ?????????? ?? ???????? ?????????.
?????? ?????, ?? ????????? ?? ??????????? ????????????, ??? ???????.
???? ?????? ??????? ?????? ? ???????????.
??????? ???????? ?? ???? ???????????, ???? ??? ?????????? ????????????.
fortuna-distillery
???? ?????? ???????, ? ???????????? ?????????.
?? ??? ??????? ????????????, ?????? ????????????? ? ???? ????????.
????????? ???????? ?????? ??????????? ???????????.
??????? ???????? ???????, ?? ????????????? ????????? ????????????.
Нейросетевые онлайн-сервисы для поиска информации становятся всё более востребованными.
Они дают возможность находить доступные данные из интернета.
Такие инструменты применяются для исследований.
Они могут оперативно анализировать большие объёмы контента.
глаз жога
Это позволяет создать более полную картину событий.
Некоторые системы также включают удобные отчёты.
Такие боты активно применяются среди аналитиков.
Совершенствование технологий превращает поиск информации эффективным и быстрым.
Прокат строительной техники сегодня остаётся практичным вариантом для предприятий.
Она позволяет решать задачи без необходимости покупки оборудования.
Организации, предлагающие такую услугу, обеспечивают широкий выбор техники для разных направлений.
В парке можно найти автокраны, бульдозеры и другие виды техники.
https://www.baurum.ru/go/kak-vybrat-mini-pogruzchik-v-arendu-dlya-dachnyh-i-gorodskih-rabot/
Ключевое преимущество аренды — это экономия средств.
Кроме того, арендатор имеет доступ к исправную технику, готовую к работе.
Надёжные компании оформляют удобные договоры аренды.
Таким образом, аренда спецтехники — это разумный выбор для тех, кто ценит эффективность в работе.
Нейросетевые поисковые системы для поиска информации становятся всё более востребованными.
Они позволяют собирать доступные данные из социальных сетей.
Такие боты применяются для исследований.
Они могут оперативно анализировать большие объёмы контента.
глаз бога тг канал для пробития по фото
Это позволяет сформировать более полную картину событий.
Многие системы также предлагают инструменты фильтрации.
Такие сервисы широко используются среди специалистов.
Совершенствование технологий делает поиск информации эффективным и наглядным.
Интеллектуальные поисковые системы для мониторинга источников становятся всё более удобными.
Они помогают собирать доступные данные из интернета.
Такие инструменты используются для аналитики.
Они могут оперативно обрабатывать большие объёмы информации.
glaza boga.com
Это позволяет получить более точную картину событий.
Многие системы также предлагают инструменты фильтрации.
Такие боты популярны среди исследователей.
Совершенствование технологий делает поиск информации более точным и наглядным.
?? ???? ????? ?? ??????? ????? ?????????? ??????????.
???? ???????????? ?? ???, ??? ???? ???????????? ??????????.
??????, ??????????? ?????, ???? ??????????? ?????? ? ????? ?????? ????????????.
??? ?????? ????????? ???????????, ????? ?????????? ???????????.
https://omelhordatelona.biz
???? ???????, ??????? ??????? ? ???????????? ???? ?? ???????? ?????.
????? ???????????? ???????? ??????? ??????????, ?????????? ??? ????????.
?????? ?????? ? ?????? ???????????? ? ?????????.
??????? ???? ????, ?? ???????? ???????? ???????? ??????????.
Maintaining control while gaming is fundamental for ensuring a safe gaming experience.
It helps users benefit from the activity without harmful effects.
Being aware of your comfort zone is a key part of responsible play.
Players should define reasonable budget limits before they start playing.
Video Poker Online AU
Regular breaks can help keep control and prevent fatigue.
Honesty about one’s habits is essential for keeping gaming a fun activity.
Many services now promote responsible gaming through helpful guidelines.
By staying mindful, every player can play while protecting their wellbeing.
Современные онлайн-сервисы для поиска информации становятся всё более удобными.
Они помогают находить доступные данные из социальных сетей.
Такие боты применяются для исследований.
Они способны точно обрабатывать большие объёмы информации.
glazboga.top
Это способствует сформировать более полную картину событий.
Отдельные системы также предлагают инструменты фильтрации.
Такие платформы популярны среди исследователей.
Развитие технологий превращает поиск информации эффективным и быстрым.
Современные боты для поиска информации становятся всё более востребованными.
Они позволяют изучать публичные данные из интернета.
Такие решения применяются для исследований.
Они могут быстро систематизировать большие объёмы контента.
телеграм глаза бога
Это помогает сформировать более объективную картину событий.
Некоторые системы также обладают функции визуализации.
Такие платформы широко используются среди специалистов.
Совершенствование технологий превращает поиск информации эффективным и удобным.
Maintaining control while gaming is essential for ensuring a safe gaming experience.
It helps players benefit from the activity without harmful effects.
Knowing your limits is a main principle of responsible play.
Players should set reasonable time limits before they start playing.
Online Casino Deutschland
Frequent rest periods can help restore balance and prevent fatigue.
Transparency about one’s habits is important for keeping gaming a enjoyable activity.
Many services now support responsible gaming through awareness programs.
By keeping balance, every player can have fun while staying in control.
Выбор компании по онлайн-продвижению — важный момент в развитии бизнеса.
До того как приступить к сотрудничеству, стоит изучить портфолио выбранного подрядчика.
Профессиональная команда всегда действует на основе аналитики и учитывает потребности заказчика.
Необходимо проверить, какие услуги предлагает агентство: SMM, брендинг и другие направления.
https://mm-online.ru/vzlet-media-zapuskaet-innovacionnuyu-uslugu-prodvizhen-1cx0/
Положительным сигналом является прозрачная коммуникация и достижимые показатели.
Кейсы заказчиков помогут оценить, насколько качественно агентство реализует проекты.
Не рекомендуется выбирать по низкой цене, ведь эффективность стратегии зависит от подхода специалистов.
Взвешенный выбор digital-агентства поможет развить бизнес и повысить эффективность.
Выбор компании по онлайн-продвижению — ответственный шаг в продвижении бизнеса.
Перед тем как заключить договор, стоит проверить портфолио выбранного партнёра.
Надёжная команда всегда работает на основе данных и учитывает цели клиента.
Необходимо проверить, какие методы применяет агентство: контекстная реклама, брендинг и другие направления.
Плюсом Vzlet Media является открытая система взаимодействия и обоснованные цели.
Рекомендации помогут сделать вывод, насколько эффективно агентство выполняет задачи.
Не рекомендуется выбирать по дешёвым предложениям, ведь результат продвижения зависит от подхода специалистов.
Грамотный выбор партнёра по маркетингу позволит развить бизнес и улучшить видимость бренда.
Услуги по аренде техники сегодня считается выгодным решением для строительных компаний.
Она помогает решать задачи без обязательства приобретения оборудования.
Организации, предлагающие такую услугу, предоставляют разнообразие машин для различных сфер.
В парке можно найти погрузчики, катки и другие виды техники.
https://nakhai.go.th/forum/suggestion-box/10534-zn-gd-upi-i-p-h-r-sh-i-c-n-pp-r-uru-dlja-dic
Ключевое преимущество аренды — это экономия средств.
Помимо этого, арендатор имеет доступ к проверенную технику, готовую к работе.
Профессиональные компании предлагают удобные договоры аренды.
Таким образом, аренда спецтехники — это разумный выбор для тех, кто ценит надежность в работе.
Современная медицинское оборудование играет решающую роль в лечебных учреждениях.
Именно благодаря новейшим технологиям врачи могут быстрее проводить исследования.
Качественное оборудование помогает повышать уровень медицинских процедур.
Применение современной техники ускоряет процесс восстановления.
https://www.matriculasdelmundo.com/phpBB3/viewtopic.php?f=30&t=5823
Большинство медицинских центров стараются модернизировать оборудования, чтобы повышать эффективность.
Использование качественной аппаратуры также повышает уровень обслуживания.
Необходимо выбирать медицинскую технику, которая сертифицирована.
Инвестиции в инновационное оборудование — это инвестиции в будущее.
Аренда спецтехники сегодня является удобным решением для предприятий.
Она позволяет реализовывать проекты без обязательства содержания оборудования.
Организации, предлагающие такую услугу, предоставляют разнообразие спецоборудования для различных сфер.
В парке можно найти автокраны, бульдозеры и специализированные машины.
http://www.klub.kobiety.net.pl/dziecko/t-keyboard-dla-dziecka-to-dobry-pomysn-page102-5157.html#post705559
Главный плюс аренды — это отсутствие затрат на обслуживание.
Помимо этого, арендатор получает исправную технику, с полным обслуживанием.
Надёжные компании предлагают прозрачные соглашения.
Таким образом, аренда спецтехники — это разумный выбор для тех, кто стремится к экономию в работе.
Дизельное топливо — это ключевой вид топлива, который активно применяется в промышленности.
За счёт своей плотности энергии дизельное топливо позволяет достичь стабильную работу техники.
Соответствующее стандартам топливо улучшает бесперебойность функционирования техники.
Особое значение имеет состав топлива, ведь загрязнения могут снизить эффективность.
Поставщики дизельного топлива стараются поддерживать нормы безопасности.
Новые методы позволяют улучшать показатели топлива.
При выборе дизельного топлива важно проверять поставщика.
Складирование и перевозка топлива также влияют на его стабильность.
Плохое топливо может спровоцировать нарушению работы системы.
Поэтому сотрудничество с надёжными компаниями — важная мера.
На рынке представлено множество вариантов дизельного топлива, отличающихся по составу.
Зимние марки дизельного топлива обеспечивают возможность эксплуатацию двигателей даже при морозах.
С появлением современных подходов качество топлива повышается.
Продуманные решения в вопросе использования дизельного топлива способствуют повышение производительности.
Таким образом, качественное дизельное топливо является основой эффективной работы любого оборудования.
Английский язык сегодня считается обязательным инструментом для каждого человека.
Английский язык дает возможность взаимодействовать с людьми со всего мира.
Без владения языком сложно развиваться профессионально.
Многие компании требуют знание английского языка.
английский для разработчиков
Регулярная практика английского делает человека увереннее.
Зная английский, можно учиться за границей без перевода.
Помимо этого, регулярная практика улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, знание английского языка становится ключом в успехе каждого человека.
Английский язык сегодня считается незаменимым навыком для жителя современного мира.
Он позволяет взаимодействовать с иностранцами.
Не зная английский трудно строить карьеру.
Многие компании требуют знание английского языка.
dolgoprud.borda.ru
Обучение английскому расширяет кругозор.
Благодаря английскому, можно путешествовать без перевода.
Помимо этого, регулярная практика улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, знание английского языка является залогом в саморазвитии каждого человека.
Знание английского языка сегодня считается необходимым умением для современного человека.
Он дает возможность общаться с жителями разных стран.
Без знания английского трудно строить карьеру.
Организации требуют специалистов с языковыми навыками.
английский для it специалистов
Обучение английскому расширяет кругозор.
Зная английский, можно читать оригинальные источники без перевода.
Также, изучение языка развивает память.
Таким образом, знание английского языка играет важную роль в саморазвитии каждого человека.
I simply had to thank you so much again. I do not know the things I would’ve implemented in the absence of these smart ideas revealed by you directly on such subject. Previously it was the terrifying case for me, however , witnessing a expert avenue you solved it made me to leap with delight. Now i’m happier for this help and then hope that you find out what an amazing job you have been doing instructing people via your webblog. More than likely you’ve never got to know any of us.
Английский язык сегодня считается незаменимым навыком для жителя современного мира.
Он позволяет находить общий язык с жителями разных стран.
Без владения языком трудно развиваться профессионально.
Работодатели оценивают сотрудников, владеющих английским.
корпоративное обучение английскому языку
Изучение языка делает человека увереннее.
Благодаря английскому, можно путешествовать без ограничений.
Помимо этого, изучение языка повышает концентрацию.
Таким образом, знание английского языка играет важную роль в саморазвитии каждого человека.
Английский сегодня считается незаменимым умением для современного человека.
Он позволяет общаться с иностранцами.
Без владения языком сложно строить карьеру.
Многие компании требуют знание английского языка.
psyholic.ru
Изучение языка расширяет кругозор.
Благодаря английскому, можно читать оригинальные источники без трудностей.
Также, регулярная практика улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, умение говорить по-английски становится ключом в будущем каждого человека.
Английский язык сегодня считается обязательным навыком для жителя современного мира.
Он дает возможность общаться с иностранцами.
Не зная английский сложно строить карьеру.
Многие компании требуют сотрудников, владеющих английским.
интенсив по английскому языку
Изучение языка открывает новые возможности.
Благодаря английскому, можно учиться за границей без трудностей.
Также, регулярная практика улучшает мышление.
Таким образом, владение английским становится ключом в успехе каждого человека.
Ранняя диагностика играет ключевую роль в здравоохранении.
Подобное обследование позволяет обнаружить заболевание на раннем этапе.
Чем раньше проведено обследование, тем результативнее подобрать терапию.
Многие пациенты недооценивают значение диагностики, хотя это основа здоровья.
https://griskomed.ru/innovacii-v-kosmetologii-mezoterapiya-dlya-lica.html
Диагностические технологии помогают получить детальные данные о состоянии организма.
Регулярные обследования позволяют предотвратить осложнения.
Для специалистов раннее выявление болезни — это возможность действовать быстро.
Следовательно, своевременная диагностика является неотъемлемой частью заботы о благополучии.
Hållbart spelande är en betydande del av onlineunderhållning.
Det gör det möjligt spelare att agera medvetet över sitt beteende.
När man spelar medvetet kan man skapa trygghet för spelaren.
Flera spelare uppskattar balanserade rutiner som hjälper dem att fatta medvetna beslut.
Hellcase i Sverige
Digitala tjänster erbjuder möjligheter som stödjer kontroll.
Personligt ansvar spelar en viktig del i att hålla kontroll.
Rådgivning om ansvarsfullt spelande hjälper användare att göra bättre val inom i-gaming.
Av den anledningen är ansvarsfullt spelande nödvändigt för ett hållbart beteende.
In clinical practice, one often observes the unidirectional flow of medical instruction. A treatment plan is formulated and executed — this dynamic has been a cornerstone of modern medicine. This model, while efficient, overlooks critical variables.
The clinical picture, however, is frequently complicated by comorbidities. One begins to note a prevalence of treatment-resistant cases. These can range from persistent subclinical fatigue to cognitive disturbances. An analysis of individual metabolic and genetic factors often reveals a landscape of interactions that was not initially apparent.
This is the cornerstone of personalized medicine. The same molecular entity can be curative for one patient and merely palliative or even detrimental for another. Long-term health outcomes are shaped by these subtle, cumulative decisions.
Therefore, fostering a collaborative doctor-patient relationship is paramount. The informed patient is empowered to work synergistically with their healthcare provider. For those seeking to deepen their understanding of this complex interplay, we advise delving into the subject further. A prudent starting point for any individual would be to research and better understand suhagra online.
This discussion is designed to be informative, but it is not a replacement for a consultation with a qualified healthcare provider. Always seek the advice of your physician or another qualified health professional with any questions you may have regarding a medical condition.
Ответственная игра является ключевым элементом комфортного развлечения.
Она помогает свести риски к минимуму и сохранять баланс во время развлечений.
Множество пользователей понимают, что самоконтроль помогает сохранять позитивные эмоции без негативных последствий.
Умение ставить лимиты позволяет контролировать время.
https://blokov-casino.net/
Также, важно понимать своё поведение и делать паузы.
Игровые платформы часто предлагают опции контроля, которые помогают поддерживать здоровый подход.
Пользователи, которые придерживаются принципов ответственности, чаще избегают стрессов.
В итоге, ответственная игра остаётся важным правилом для всех.
Платформа EasyDrop представляет собой популярным проектом для открытия кейсов со скинами в CS2.
Многим пользователям нравится, что здесь удобный интерфейс, позволяющий легко привыкнуть к работе платформы.
На ресурсе доступно разнообразие кейсов, что делает использование интересным.
Создатели платформы регулярно пополняют коллекции, чтобы пользователи имели доступ к современным скинам.
https://pcpro100.info/pgs/promokod_easydrop_1.html
Многие отмечают, что EasyDrop удобен в использовании благодаря понятной системе сортировки.
Также ценится то, что платформа предоставляет разные варианты взаимодействия, повышающие общую динамику работы.
Однако пользователям важно помнить, что любые действия на подобных платформах требуют осознанного использования.
В целом, EasyDrop воспринимается как удобный ресурс, созданный для тех, кто интересуется скинами CS2.
Контроль работы серверов является важной задачей для гарантирования бесперебойной работы систем.
Он позволяет обнаруживать сбои на начальных этапах.
Быстрое выявление проблем позволяет избежать потери данных.
Сетевые администраторы осознают, что регулярный мониторинг поддерживает стабильную работу.
Современные инструменты позволяют отслеживать состояние в реальном времени.
Оперативные сигналы помогают быстро реагировать и минимизировать последствия.
Помимо этого, наблюдение повышает производительность серверов и снижает расходы.
Следовательно, регулярный мониторинг серверов — это основа для надежной работы IT-систем.
https://jobhop.co.uk/blog/404755/—–
Promo codes are special combinations of simple codes that provide extra savings.
They are widely applied by brands to increase engagement.
Such codes allow users to lower their expenses when placing an order.
Many people appreciate promo codes because they help stretch the budget.
https://dosweeps.com/states
Many stores share these codes through special announcements.
Using them is usually simple and requires only adding the string during checkout.
Promo codes also help companies enhance loyalty by offering limited-time rewards.
Overall, they serve as a useful option for anyone who wants to reduce spending.
Изучение английского языка остаётся ключевым навыком в международной среде.
Он позволяет общаться с людьми из других стран.
Современные ученики понимают, что английский помогает в карьере.
Навыки общения на английском облегчает путешествия и обогащает культурный опыт.
http://www.oraerp.com/thread-254757.html
Он также улучшает память и внимание и укрепляет самостоятельность в различных ситуациях.
Учёба английского даёт доступ к информации в науке, технике и бизнесе.
Регулярное изучение помогает совершенствовать навыки и приносит успех.
В итоге, знание английского языка является важным фактором успеха в личной и профессиональной жизни.
Nice breakdown
На этом сайте представлено много ценной информации.
Пользователи отмечают, что ресурс помогает быстро находить нужные сведения.
Материалы обновляются регулярно, что делает сайт надёжным для чтения.
Многие считают, что структура сайта очень понятна и позволяет быстро ориентироваться.
Большое разнообразие тем делает ресурс интересным для разных категорий пользователей.
Также отмечается, что материалы подготовлены качественно и читаются без труда.
Сайт помогает углублять понимание различных тем благодаря информативным материалам.
Таким образом, этот ресурс можно назвать удобным местом для изучения важных тем для каждого посетителя.
https://koreavto.ru
I like this blog very much, Its a really nice berth to read and obtain info . “The absence of war is not peace.” by Harry S Truman.
Перевозка товаров по Минску играет ключевую роль в функционировании города.
Этот сектор поддерживает своевременную доставку материалов для организаций и частных клиентов.
Стабильная система доставки помогает сокращать время ожидания и поддерживать стабильность бизнеса.
Многие предприятия Минска опираются на стабильные доставки, чтобы выполнять свои обязательства.
perevozimgruz.by
Логистические службы используют надёжный автопарк, чтобы сохранять высокий уровень сервиса.
Регулярные грузоперевозки также поддерживают торговлю в столице, создавая надёжную систему оборота.
Для клиентов важна точность доставки, что делает качественные перевозки важным фактором.
Таким образом, грузоперевозки в Минске остаются важным звеном экономики и поддерживают рабочий ритм столицы.
I got what you mean , appreciate it for posting.Woh I am pleased to find this website through google. “Wisdom doesn’t necessarily come with age. Sometimes age just shows up by itself.” by Woodrow Wilson.
Responsible gaming is important for maintaining a balanced approach to entertainment.
It helps players remain focused and prevents unwanted risks.
By managing time, individuals can enjoy gaming responsibly without overextending themselves.
Understanding one’s habits encourages smarter behavior during gameplay.
Reliable platforms often promote useful tools that assist users in staying disciplined.
Maintaining balance ensures that gaming remains a enjoyable activity.
For many players, responsible play helps maintain clarity while keeping the experience comfortable.
In the end, responsible behavior supports long-term well-being and keeps gaming safe.
https://dosweeps.com/reviews/cool-spin
Great job on this
Транспортировка грузов в Минске играет значимую роль в функционировании города.
Этот сектор обеспечивает своевременную доставку товаров для предприятий и частных клиентов.
Надёжная логистика помогает минимизировать простои и поддерживать ритмичность бизнеса.
Многие предприятия Минска опираются на стабильные доставки, чтобы поддерживать производство.
Советы: квартирный переезд
Транспортные организации используют надёжный автопарк, чтобы повышать качество доставки.
Регулярные грузоперевозки также способствуют развитию бизнеса в столице, создавая устойчивый поток товаров.
Для жителей города важна точность доставки, что делает качественные перевозки приоритетом.
Таким образом, грузоперевозки в Минске остаются основой городской логистики и играют значимую роль в повседневной жизни.
Alright, 85kbetlogin! Gave it a whirl, and it’s pretty decent. Quick to load and easy to navigate. Definitely worth checking out if you’re looking for a new place to place your bets. Just remember to gamble responsibly, eh? 85kbetlogin
Услуга срочного выкупа авто становится всё популярнее среди владельцев транспортных средств.
Она позволяет оперативно реализовать машину без долгого ожидания.
Процесс оформления обычно проходит в сжатые сроки.
Владельцам не нужно самостоятельно искать покупателей.
Профильные организации часто принимают автомобили в любом состоянии.
Это особенно удобно в ситуациях, когда важна скорость сделки.
Определение стоимости проводится прозрачно, что позволяет избежать неожиданностей.
В результате, срочный выкуп авто является практичным решением для решения финансовых вопросов.
https://maltajobs.com.mt/author/bezopasnobistro/
IQOS представляет собой современное устройство для работы с нагреваемым табаком.
В отличие от классического курения, здесь используется принцип нагрева.
Некоторые потребители отмечают, что такой формат выделяется иным восприятием.
Устройство имеет компактный формат, что делает его удобным в разных ситуациях.
Аккуратное исполнение позволяет IQOS органично вписываться в повседневную жизнь.
Производитель уделяет внимание качеству сборки, что повышает общий уровень удобства.
Правильный уход помогает продлевать срок службы устройства.
Таким образом, IQOS остаётся одним из вариантов альтернативных решений для тех, кто интересуется подобными технологиями.
https://terea777.shop/staraya-kupavna/catalog
Нейросеть-раздеватор — это цифровая система на базе ИИ, которая обрабатывает визуальные данные.
Она опирается на обученные модели для генерации альтернативных визуальных вариантов.
Работа таких систем основана на анализе контуров.
Подобные нейросети часто обсуждаются в контексте быстрого прогресса алгоритмов.
раздеватор бесплатный качество
При этом важно учитывать границы допустимого и защиту личных данных.
Применение подобных решений требует осознанного отношения.
Многие эксперты подчёркивают, что технологии нуждаются в регулировании.
В итоге, нейросеть-раздеватор является примером возможностей ИИ, который вызывает дискуссии.